A mutant Ahr allele protects the embryonic kidney from hydrocarbon-induced deficits in fetal programming
- PMID: 21803694
- PMCID: PMC3261986
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1103692
A mutant Ahr allele protects the embryonic kidney from hydrocarbon-induced deficits in fetal programming
Abstract
Background: The use of experimental model systems has expedited the elucidation of pathogenetic mechanisms of renal developmental disease in humans and the identification of genes that orchestrate developmental programming during nephrogenesis.
Objectives: We conducted studies to evaluate the role of AHR polymorphisms in the disruption of renal developmental programming by benzo(a)pyrene (BaP).
Methods: We used metanephric cultures of C57BL/6J (C57) mice expressing the Ahr(b-1) allele and B6.D2N-Ahr(d)/J (D2N) mice expressing a mutant allele deficient in ligand binding (Ahr(d)) to investigate molecular mechanisms of renal development. Deficits in fetal programming were evaluated in the offspring of pregnant mice treated with BaP during nephrogenesis.
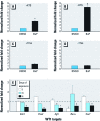
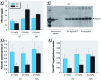
Results: Hydrocarbon challenge of metanephri from C57 mice altered Wilms' tumor suppressor gene (Wt1) mRNA splice variant ratios and reduced mRNAs of the Wt1 transcriptional targets syndecan-1 (Sdc1) paired box gene 2 (Pax2), epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr), and retinoic acid receptor, alpha (Rarα). These changes correlated with down-regulation of effectors of differentiation [secreted frizzled-related sequence protein 1 (Sfrp1), insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (Igf1r), wingless-related MMTV-integration site 4 (Wnt4), Lim homeobox protein 1 (Lhx1), E-cadherin]. In contrast, metanephri from D2N mice were spared hydrocarbon-induced changes in Wt1 splice variant ratios and deficits of differentiation. We observed similar patterns of dysmorphogenesis and progressive loss of renal function at postnatal weeks 7 and 52 in the offspring of pregnant C57 but not D2N mice gavaged with 0.1 or 0.5 mg/kg BaP on gestation days 10-13.
Conclusions: These findings support a functional link between AHR and WT1 in the regulation of renal morphogenesis and raise important questions about the contribution of human AHR polymorphisms to the fetal origins of adult-onset kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
AHR regulates WT1 genetic programming during murine nephrogenesis.Mol Med. 2011;17(11-12):1275-84. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00125. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21863216 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-activated Ahr signaling leads to disruption of nephrogenesis and altered Wilms' tumor suppressor mRNA splicing.Oncogene. 2003 Apr 10;22(14):2160-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206238. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12687018
-
Genetic regulatory networks of nephrogenesis: deregulation of WT1 splicing by benzo(a)pyrene.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2009 Jun;87(2):192-7. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20148. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2009. PMID: 19530133 Review.
-
Epigenetic control of embryonic renal cell differentiation by L1 retrotransposon.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2011 Aug;91(8):693-702. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20786. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2011. PMID: 21384534 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of biological regulatory networks during nephrogenesis.Drug Metab Rev. 2006;38(4):677-83. doi: 10.1080/03602530600959532. Drug Metab Rev. 2006. PMID: 17145695 Review.
Cited by
-
In utero exposure to benzo(a)pyrene predisposes offspring to cardiovascular dysfunction in later-life.Toxicology. 2012 May 16;295(1-3):56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.01.017. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22374506 Free PMC article.
-
AHR regulates WT1 genetic programming during murine nephrogenesis.Mol Med. 2011;17(11-12):1275-84. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00125. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21863216 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): "pioneer member" of the basic-helix/loop/helix per-Arnt-sim (bHLH/PAS) family of "sensors" of foreign and endogenous signals.Prog Lipid Res. 2017 Jul;67:38-57. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28606467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic reactivation of LINE-1 retrotransposon disrupts NuRD corepressor functions and induces oncogenic transformation in human bronchial epithelial cells.Mol Oncol. 2018 Aug;12(8):1342-1357. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12329. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29845737 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory effects of catechin hydrate on benzo[a]pyrene-induced nephrotoxicity in adult male albino rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 May 17;10(3):542-550. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab029. eCollection 2021 May. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34141168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avner ED. Renal developmental diseases. Semin Nephrol. 1993;13:427–435. - PubMed
-
- Barbaux S, Niaudet P, Gubler M-C, Grünfeld J-P, Jaubert F, Kuttenn F, et al. Donor splice-site mutations in WT1 are responsible for Frasier syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997;17:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJP. The developmental origins of adult disease. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004;23(suppl 6):588S–595S. - PubMed
-
- Barnes JD, Crosby JL, Jones CM, Wright CVE, Hogan BLM. Embryonic expression of Lim-1, the mouse homolog of Xenopus XLim-1, suggests a role in lateral mesoderm differentiation and neurogenesis. Dev Biol. 1994;161:168–178. - PubMed
-
- Bertazzi PA, Pesatori AC, Zocchetti C, Latocca R. Mortality study of cancer risk among oil refinery workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1989;61(4):261–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

