Combinatorial treatments that overcome PDGFRβ-driven resistance of melanoma cells to V600EB-RAF inhibition
- PMID: 21803746
- PMCID: PMC3149831
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0140
Combinatorial treatments that overcome PDGFRβ-driven resistance of melanoma cells to V600EB-RAF inhibition
Abstract
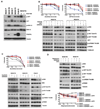
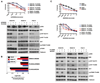
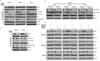
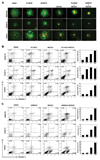
(V600E)B-RAF mutation is found in 50% to 60% of melanomas, and the novel agents PLX4032/vemurafenib and GSK2118436 that inhibit the (V600E)B-RAF kinase achieve a remarkable clinical response rate. However, as might be expected, acquired clinical resistance to these agents arises in most melanoma patients. PLX4032/vemurafenib resistance that arises in vivo in tumor matched short-term cultures or in vitro in melanoma cell lines is not caused by acquisition of secondary mutations in (V600E)B-RAF but rather is caused by upregulating platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ) or N-RAS which results in resistance or sensitivity to mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated (ERK; MEK) kinase inhibitors, respectively. In this study, we define a targeted combinatorial strategy to overcome PLX4032/vemurafenib resistance in melanoma cell lines or short-term culture where the resistance is driven by PDGFRβ upregulation, achieving synergistic growth inhibition and cytotoxicity. PDGFRβ-upregulated, PLX4032-resistant (PPRM) cell lines show dual phospho (p)-ERK and p-AKT upregulation, and their growth inhibitory responses to specific small molecule inhibitors correlated with p-ERK, p-AKT, and p-p70S6K levels. Coordinate inhibition of (V600E)B-RAF inhibition and the RTK-PI3K-AKT-mTORC axis led to functionally significant rebound signaling, illustrating a robust and dynamic network connectivity. Combined B-RAF, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and mTORC1/2 inhibition suppressed both immediate early and delayed compensatory signaling, resulting in a highly synergistic growth inhibitory response but less efficient cytotoxic response. In contrast, the combination of MEK1/2, PI3K, and mTORC1/2 inhibitors consistently triggered apoptosis in a highly efficient manner. Together, our findings offer a rational strategy to guide clinical testing in preidentified subsets of patients who relapse during treatment with (V600E)B-RAF inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

