The extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathway regulates expression of renal D1 dopamine receptors in diabetic rats
- PMID: 21803776
- PMCID: PMC3173236
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.268136
The extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathway regulates expression of renal D1 dopamine receptors in diabetic rats
Abstract
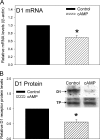
Activation of D1 dopamine receptors expressed in the kidneys promotes the excretion of sodium and regulates sodium levels during increases in dietary sodium intake. A decrease in the expression or function of D1 receptors results in increased sodium retention which can potentially lead to the development of hypertension. Studies have shown that in the absence of functional D1 receptors, in null mice, the systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures are higher. Previous studies have shown that the expression and function of D1 receptors in the kidneys are decreased in animal models of diabetes. The mechanisms that down-regulate the expression of renal D1 receptor gene in diabetes are not well understood. Using primary renal cells and acutely isolated kidneys from the streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic model, we demonstrate that the renal D1 receptor expression is down-regulated by the extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathway in vitro and in vivo. In cultures of primary renal cells, a 3 mm, 60-h cAMP treatment down-regulated the expression of D1 receptors. In vivo, we determined that the plasma and urine cAMP levels as well as the expression of 5'-ectonucleotidase, tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase, and adenosine A2a receptors are significantly increased in diabetic rats. Inhibitors of 5'-ectonucleotidase and tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase, α,β-methyleneadenosine 5'-diphosphate, and levamisole, respectively, blocked the down-regulation of D1 receptors in the primary renal cells and in the kidney of diabetic animals. The results suggest that inhibitors of the extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathway reverse the down-regulation of renal D1 receptor in diabetes.
Figures


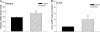


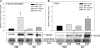



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

