Plasmids of raw milk cheese isolate Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis DPC3901 suggest a plant-based origin for the strain
- PMID: 21803914
- PMCID: PMC3187126
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00661-11
Plasmids of raw milk cheese isolate Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis DPC3901 suggest a plant-based origin for the strain
Abstract
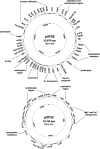
The four-plasmid complement of the raw milk cheese isolate Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis DPC3901 was sequenced, and some genetic features were functionally analyzed. The complete sequences of pVF18 (18,977 bp), pVF21 (21,739 bp), pVF22 (22,166 bp), and pVF50 (53,876 bp) were obtained. Each plasmid contained genes not previously described for Lactococcus, in addition to genes associated with plant-derived lactococcal strains. Most of the novel genes were found on pVF18 and encoded functions typical of bacteria associated with plants, such as activities of plant cell wall modification (orf11 and orf25). In addition, a predicted high-affinity regulated system for the uptake of cobalt was identified (orf19 to orf21 [orf19-21]), which has a single database homolog on a plant-derived Leuconostoc plasmid and whose functionality was demonstrated following curing of pVF18. pVF21 and pVF22 encode additional metal transporters, which, along with orf19-21 of pVF18, could enhance host ability to uptake growth-limiting amounts of biologically essential ions within the soil. In addition, vast regions from pVF50 and pVF21 share significant homology with the plant-derived lactococcal plasmid pGdh442, which is indicative of extensive horizontal gene transfer and recombination between these plasmids and suggests a common plant niche for their hosts. Phenotypes associated with these regions include glutamate dehydrogenase activity and Na(+) and K(+) transport. The presence of numerous plant-associated markers in L. lactis DPC3901 suggests a plant origin for the raw milk cheese isolate and provides for the first time the genetic basis to support the concept of the plant-milk transition for Lactococcus strains.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sequence analysis of the mobilizable lactococcal plasmid pGdh442 encoding glutamate dehydrogenase activity.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 May;153(Pt 5):1664-1675. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/002246-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17464081
-
Molecular characterization and structural instability of the industrially important composite metabolic plasmid pLP712.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Dec;158(Pt 12):2936-2945. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.062554-0. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 23023974
-
Complete sequences of four plasmids of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris SK11 reveal extensive adaptation to the dairy environment.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Dec;71(12):8371-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8371-8382.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16332824 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical citrate-fermenting Lactococcus lactis strains isolated from dromedary's milk.J Appl Microbiol. 2010 Feb;108(2):647-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04459.x. Epub 2009 Jul 7. J Appl Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19663815
-
Detection and classification of the integrative conjugative elements of Lactococcus lactis.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 1;25(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10255-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38561675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmids from Food Lactic Acid Bacteria: Diversity, Similarity, and New Developments.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 10;16(6):13172-202. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613172. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26068451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large plasmidome of dairy Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis FM03P encodes technological functions and appears highly unstable.BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 17;19(1):620. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5005-2. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30119641 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and evolutionary analysis of Lactococcus garvieae isolated from human endocarditis.Microb Genom. 2022 Feb;8(2):000771. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000771. Microb Genom. 2022. PMID: 35196218 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of the dairy isolate Streptococcus macedonicus ACA-DC 198 against related members of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex.BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 8;15:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-272. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24713045 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive Exclusion Bacterial Culture Derived from the Gut Microbiome of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) as a Resource to Efficiently Recover Probiotic Strains: Taxonomic, Genomic, and Functional Proof of Concept.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 8;10(7):1376. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071376. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beresford T., Condon S. 1991. Cloning and partial characterization of genes for ribosomal ribonucleic-acid in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 78:319–324 - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254 - PubMed
-
- Christensen J. E., Dudley E. G., Pederson J. A., Steele J. L. 1999. Peptidases and amino acid catabolism in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 76:217–246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

