Enhancement by LDL of transfer of L-4F and oxidized lipids to HDL in C57BL/6J mice and human plasma
- PMID: 21804067
- PMCID: PMC3173006
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M016741
Enhancement by LDL of transfer of L-4F and oxidized lipids to HDL in C57BL/6J mice and human plasma
Abstract
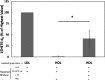
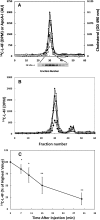
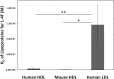
The apoA-I mimetic peptide L-4F [(Ac-D-W-F-K-A-F-Y-D-K-V-A-E-K-F-K-E-A-F-NH2) synthesized from all L-amino acids] has shown potential for the treatment of a variety of diseases. Here, we demonstrate that LDL promotes association between L-4F and HDL. A 2- to 3-fold greater association of L-4F with human HDL was observed in the presence of human LDL as compared with HDL by itself. This association further increased when LDL was supplemented with the oxidized lipid 15S-hydroxy-5Z, 8Z, 11Z, 13E-eicosatetraenoic acid (15HETE). Additionally, L-4F significantly (P = 0.02) promoted the transfer of 15HETE from LDL to HDL. The transfer of L-4F from LDL to HDL was demonstrated both in vitro and in C57BL/6J mice. L-4F, injected into C57BL/6J mice, associated rapidly with HDL and was then cleared quickly from the circulation. Similarly, L-4F loaded onto human HDL and injected into C57BL/6J mice was cleared quickly with T(1/2) = 23.6 min. This was accompanied by a decline in human apoA-I with little or no effect on the mouse apoA-I. Based on these results, we propose that i) LDL promotes the association of L-4F with HDL and ii) in the presence of L-4F, oxidized lipids in LDL are rapidly transferred to HDL allowing these oxidized lipids to be acted upon by HDL-associated enzymes and/or cleared from the circulation.
Figures






References
-
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Jones J. L., Brouillette C. G., Schmidt C. F., Chung B. H., Hughes T. A, Bhown A. S., Segrest J. P. 1985. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Structure of complexes with dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 10248–10255. - PubMed
-
- Anantharamaiah G. M. 1986. Synthetic peptide analogs of apolipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 128: 627–647. - PubMed
-
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr 1974. A molecular theory of lipid-protein interactions in the plasma lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 38: 247–258. - PubMed
-
- Segrest J. P., Jones M. K., De Loof H., Brouillette C. G., Venkatachalapathi Y. V., Anantharamaiah G. M. 1992. The amphipathic helix in the exchangeable apolipoproteins: a review of secondary structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 33: 141–166. - PubMed
-
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Mishra V. K., Garber D. W., Datta G., Handattu S. P., Palgunachari M. N., Chaddha M., Navab M., Reddy S. T., Segrest J. P., et al. 2007. Structural requirements for antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides. J. Lipid Res. 48: 1915–1923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

