Activation of RhoA in podocytes induces focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 21804090
- PMCID: PMC3171934
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010111146
Activation of RhoA in podocytes induces focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
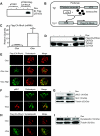
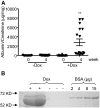
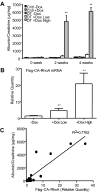
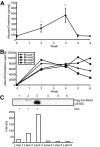
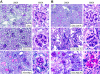
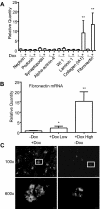
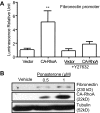
Proper organization of the actin cytoskeleton is essential for the normal structure and function of podocytes. RhoA modulates actin dynamics but its role in podocyte biology is controversial. Here, we generated transgenic mice that express a constitutively active form of RhoA in a podocyte-specific and doxycycline-inducible manner. Induction of activated RhoA with doxycycline resulted in significant albuminuria. Furthermore, both the degree of albuminuria and the histologic changes in the glomerulus positively correlated with the level of constitutively active RhoA expression: low levels of expression associated with segmental foot-process effacement without changes observable by light microscopy, whereas higher levels of expression associated with both extensive foot-process effacement and histologic features of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). In addition, induction of activated RhoA markedly upregulated glomerular mRNA expression of fibronectin and collagen IA1, and the degree of upregulation positively correlated with the level of albuminuria. Withdrawal of doxycycline led to a decline in albuminuria toward basal levels in most mice, but heavy albuminuria persisted in some mice. Taken together, these data suggest that activation of RhoA in podocytes leads to albuminuria accompanied by a range of histologic changes characteristic of minimal change disease and FSGS in humans. Although most changes are reversible, severe and prolonged activation of RhoA may cause irreversible glomerulosclerosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SRGAP1 Controls Small Rho GTPases To Regulate Podocyte Foot Process Maintenance.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Mar;32(3):563-579. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020081126. Epub 2021 Jan 29. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33514561 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin therapy ameliorates podocytopathy and proteinuria in experimental focal segmental glomerulosclerosis involving a podocyte specific non-MC1R-mediated melanocortinergic signaling.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Apr 17;134(7):695-710. doi: 10.1042/CS20200016. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32167144 Free PMC article.
-
Mice with mutant Inf2 show impaired podocyte and slit diaphragm integrity in response to protamine-induced kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2016 Aug;90(2):363-372. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27350175 Free PMC article.
-
The spectrum of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: new insights.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008 May;17(3):271-81. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3282f94a96. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008. PMID: 18408478 Review.
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; why does it occur segmentally?Pflugers Arch. 2017 Aug;469(7-8):983-988. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2023-x. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28664408 Review.
Cited by
-
Gain-of-function mutations in transient receptor potential C6 (TRPC6) activate extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2).J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 21;288(25):18407-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463059. Epub 2013 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23645677 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC Channels in Proteinuric Kidney Diseases.Cells. 2019 Dec 23;9(1):44. doi: 10.3390/cells9010044. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31877991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smurf1 regulates ameloblast polarization by ubiquitination-mediated degradation of RhoA.Cell Prolif. 2023 Apr;56(4):e13387. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13387. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36579844 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid peroxidation regulates podocyte migration and cytoskeletal structure through redox sensitive RhoA signaling.Redox Biol. 2018 Jun;16:248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.024. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29547847 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Diabetic Nephropathy in Diabetic Mice by Fasudil through Regulation of Macrophage Polarization.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jun 30;2020:4126913. doi: 10.1155/2020/4126913. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32685556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faul C, Asanuma K, Yanagida-Asanuma E, Kim K, Mundel P: Actin up: Regulation of podocyte structure and function by components of the actin cytoskeleton. Trends Cell Biol 17: 428–437, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Wennerberg K: Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell 116: 167–179, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Hall A: The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 70: 389–399, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Asanuma K, Yanagida-Asanuma E, Faul C, Tomino Y, Kim K, Mundel P: Synaptopodin orchestrates actin organization and cell motility via regulation of RhoA signalling. Nat Cell Biol 8: 485–491, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

