The expression levels of stem cell markers importin13, c-kit, CD146, and telomerase are decreased in endometrial polyps
- PMID: 21804459
- PMCID: PMC3539613
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.881901
The expression levels of stem cell markers importin13, c-kit, CD146, and telomerase are decreased in endometrial polyps
Abstract
Background: To investigate the expression levels of importin13 (IPO13), c-kit, CD146, telomerase, caspase-3, bcl-2 and bax in endometrial polyps (EPs).
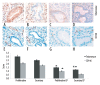
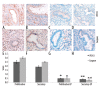
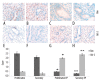
Material/methods: We detected the mRNA expression levels of IPO13, c-kit, bcl-2 and bax in endometrial polyps (EPs) using real-time PCR. We detected the protein expression levels of IPO13, telomerase, CD146, caspase-3, bcl-2 and bax in EPs using S-P (Streptavidin-Peroxidase) immunohistochemistry. Western blotting was performed to determine the levels of importin13 and bcl-2 proteins in EPs.
Results: The expression levels of IPO13, c-kit, telomerase, caspase3, and bax were lower in the EP tissue compared to normal endometrial tissue during the proliferation and secretion phases of the menstrual cycle (p<0.05). The expression of CD146 was decreased in the EP tissue compared to the normal endometrial tissue during the proliferation phase of the menstrual cycle (p<0.05). The expression of bcl-2 was increased in the EP tissue compared to the normal endometrial tissue during the proliferation and secretion phases of the menstrual cycle (p<0.05).
Conclusions: The expression levels of IPO13, c-kit, telomerase, caspase3, and bax were decreased; however, the expression of bcl-2 was increased in the EP tissue compared to the normal endometrial tissue. These findings suggest that the development of EPs is associated with the deregulated activities of the endometrial stem/progenitor cells and the decreased apoptosis of endometrial cells, with the latter being the major factor involved in the development of EPs.
Figures

References
-
- Dal Cin P, Vanni R, Marras S, et al. Four cytogenetic subgroups can be identified in endometrial polyps. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1565–68. - PubMed
-
- Taylor LJ, Jackson TL, Reid JG, Duffy SR. The differential expression of oestrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, Bcl-2 and Ki67 in endometrial polyps. BJOG. 2003;110:794–98. - PubMed
-
- de S, Almeida EC, Nogueira AA, Candido dRFJ, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors in endometrial polyps and adjacent endometrium in postmenopausal women. Maturitas. 2004;49:229–33. - PubMed
-
- Kim MR, Kim YA, Jo MY, et al. High frequency of endometrial polyps in endometriosis. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2003;10:46–48. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Medina T, Bajo-Arenas J, Haya J, et al. Tibolone and risk of endometrial polyps: a prospective, comparative study with hormone therapy. Menopause. 2003;10:534–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

