A Drosophila metallophosphoesterase mediates deglycosylation of rhodopsin
- PMID: 21804530
- PMCID: PMC3173788
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.254
A Drosophila metallophosphoesterase mediates deglycosylation of rhodopsin
Abstract
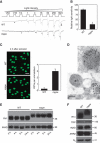
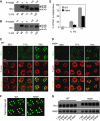
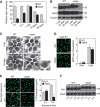
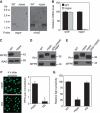
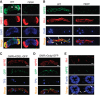
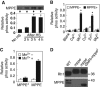
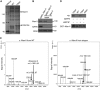
Oligosaccharide chains of newly synthesized membrane receptors are trimmed and modified to optimize their trafficking and/or signalling before delivery to the cell surface. For most membrane receptors, the functional significance of oligosaccharide chain modification is unknown. During the maturation of Rh1 rhodopsin, a Drosophila light receptor, the oligosaccharide chain is trimmed extensively. Neither the functional significance of this modification nor the enzymes mediating this process are known. Here, we identify a dmppe (Drosophila metallophosphoesterase) mutant with incomplete deglycosylation of Rh1, and show that the retained oligosaccharide chain does not affect Rh1 localization or signalling. The incomplete deglycosylation, however, renders Rh1 more sensitive to endocytic degradation, and causes morphological and functional defects in photoreceptors of aged dmppe flies. We further demonstrate that the dMPPE protein functions as an Mn(2+)/Zn(2+)-dependent phosphoesterase and mediates in vivo dephosphorylation of α-Man-II. Most importantly, the dephosphorylated α-Man-II is required for the removal of the Rh1 oligosaccharide chain. These observations suggest that the glycosylation status of membrane proteins is controlled through phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, and that MPPE acts as the phosphoesterase in this regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
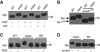
References
-
- Brown G, Chen DM, Christianson JS, Lee R, Stark WS (1994) Receptor demise from alteration of glycosylation site in Drosophila opsin: electrophysiology, microspectrophotometry, and electron microscopy. Vis Neurosci 11: 619–628 - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Yakunin AF, Kuznetsova E, Busso D, Pufan R, Proudfoot M, Kim R, Kim SH (2004) Structural and functional characterization of a novel phosphodiesterase from Methanococcus jannaschii. J Biol Chem 279: 31854–31862 - PubMed
-
- Chmelar RS, Nathanson NM (2006) Identification of a novel apical sorting motif and mechanism of targeting of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem 281: 35381–35396 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

