3'UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPβ post-translational activation and senescence in tumour cells
- PMID: 21804532
- PMCID: PMC3173785
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.250
3'UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPβ post-translational activation and senescence in tumour cells
Abstract
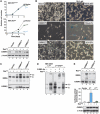
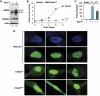
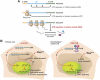
C/EBPβ is an auto-repressed protein that becomes post-translationally activated by Ras-MEK-ERK signalling. C/EBPβ is required for oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) of primary fibroblasts, but also displays pro-oncogenic functions in many tumour cells. Here, we show that C/EBPβ activation by H-Ras(V12) is suppressed in immortalized/transformed cells, but not in primary cells, by its 3' untranslated region (3'UTR). 3'UTR sequences inhibited Ras-induced cytostatic activity of C/EBPβ, DNA binding, transactivation, phosphorylation, and homodimerization, without significantly affecting protein expression. The 3'UTR suppressed induction of senescence-associated C/EBPβ target genes, while promoting expression of genes linked to cancers and TGFβ signalling. An AU-rich element (ARE) and its cognate RNA-binding protein, HuR, were required for 3'UTR inhibition. These components also excluded the Cebpb mRNA from a perinuclear cytoplasmic region that contains activated ERK1/2, indicating that the site of C/EBPβ translation controls de-repression by Ras signalling. Notably, 3'UTR inhibition and Cebpb mRNA compartmentalization were absent in primary fibroblasts, allowing Ras-induced C/EBPβ activation and OIS to proceed. Our findings reveal a novel mechanism whereby non-coding mRNA sequences selectively regulate C/EBPβ activity and suppress its anti-oncogenic functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


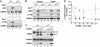



Comment in
-
C/EBPβ: lost beyond translation.EMBO J. 2011 Sep 14;30(18):3663-4. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.288. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21915145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta JC, O’Loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N, Takatsu Y, Melamed J, d’Adda di Fagagna F, Bernard D, Hernando E, Gil J (2008) Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133: 1006–1018 - PubMed
-
- Adams PD (2009) Healing and hurting: molecular mechanisms, functions, and pathologies of cellular senescence. Mol Cell 36: 2–14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

