Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via upregulation of MEKK2
- PMID: 21804577
- PMCID: PMC4003298
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.52
Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via upregulation of MEKK2
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the mechanism underlying the increase of hepatoma cell proliferation by hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx).
Methods: HepG2, H7402 and HepG2.2.15 cells, which constitutively replicated hepatitis B virus were used. The effects of HBx on hepatoma cell proliferation were examined using 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation assay and MTT assay. The expression level of MEKK2 was measured using RT-PCR, Western blot and luciferase reporter gene assay. The activity of activator protein 1 (AP-1) was detected using luciferase reporter gene assay. The phosphorylation levels of JNK and c-Jun were measured using Western blot. The expression levels of HBx and MEKK2 in 11 clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues were measured using real time PCR and Western blot. In addition, the expression of MEKK2 in 95 clinical HCC tissues was examined using immunohistochemistry.
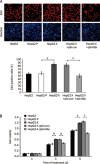
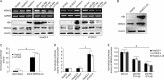
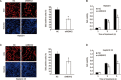
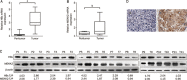
Results: HBx significantly enhanced HepG2-X cell proliferation. In HepG2-X, H7402-X and HepG2.2.15 cells, the expression level of MEKK2 was remarkably increased. In HepG2.2.15 cells, HBx was found to activate JNK and AP-1, which were the downstream effectors of MEKK2 in HepG2-X and HepG2.2.15 cells. In 11 clinical HCC tissues, both HBx and MEKK2 expression levels were remarkably increased, as compared to those in the corresponding peritumor tissues. In 95 clinical HCC tissues, the rate of detection of MEKK2 was 85.3%.
Conclusion: HBx promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via upregulating MEKK2, which may be involved in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Koike K. Hepatitis B virus X gene is implicated in liver carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2009;286:60–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Zhang H, Ye L. Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. J Lab Clin Med. 2006;147:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Liang X, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Gao L, Han L, Ma C, et al. Hepatitis B virus sensitizes hepatocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through Bax. J Immunol. 2007;178:503–10. - PubMed
-
- Shan C, Xu F, Zhang S, You J, You X, Qiu L, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell proliferation via a positive cascade loop involving arachidonic acid metabolism and p-ERK1/2. Cell Res. 2010;20:563–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

