Sources of Cognitive Exploration: Genetic Variation in the Prefrontal Dopamine System Predicts Openness/Intellect
- PMID: 21804655
- PMCID: PMC3143482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jrp.2011.04.002
Sources of Cognitive Exploration: Genetic Variation in the Prefrontal Dopamine System Predicts Openness/Intellect
Abstract
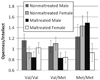
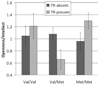
The personality trait Openness/Intellect reflects the tendency to be imaginative, curious, perceptive, artistic, and intellectual-all characteristics that involve cognitive exploration. Little is known about the biological basis of Openness/Intellect, but the trait has been linked to cognitive functions of prefrontal cortex, and the neurotransmitter dopamine plays a key role in motivation to explore. The hypothesis that dopamine is involved in Openness/Intellect was supported by examining its association with two genes that are central components of the prefrontal dopaminergic system. In two demographically different samples (children: N = 608; adults: N = 214), variation in the dopamine D4 receptor gene (DRD4) and the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene (COMT) predicted Openness/Intellect, as main effects in the child sample and in interaction in adults.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sources of openness/intellect: cognitive and neuropsychological correlates of the fifth factor of personality.J Pers. 2005 Aug;73(4):825-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2005.00330.x. J Pers. 2005. PMID: 15958136 Review.
-
COMT x DRD4 epistasis impacts prefrontal cortex function underlying response control.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Jun;23(6):1453-62. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs132. Epub 2012 May 22. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22617852
-
Openness to Experience and Intellect Differentially Predict Creative Achievement in the Arts and Sciences.J Pers. 2016 Apr;84(2):248-58. doi: 10.1111/jopy.12156. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Pers. 2016. PMID: 25487993 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia: potential role of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors.CNS Drugs. 2007;21(7):535-57. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200721070-00002. CNS Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17579498 Review.
-
Intellect as distinct from Openness: differences revealed by fMRI of working memory.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2009 Nov;97(5):883-92. doi: 10.1037/a0016615. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2009. PMID: 19857008 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biological and cognitive underpinnings of religious fundamentalism.Neuropsychologia. 2017 Jun;100:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Neuropsychologia. 2017. PMID: 28392301 Free PMC article.
-
The neuromodulator of exploration: A unifying theory of the role of dopamine in personality.Front Hum Neurosci. 2013 Nov 14;7:762. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00762. eCollection 2013. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24294198 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine and the Creative Mind: Individual Differences in Creativity Are Predicted by Interactions between Dopamine Genes DAT and COMT.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 19;11(1):e0146768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146768. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26783754 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting who takes music lessons: parent and child characteristics.Front Psychol. 2015 Mar 24;6:282. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00282. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 25852601 Free PMC article.
-
Moderation of maltreatment effects on childhood borderline personality symptoms by gender and oxytocin receptor and FK506 binding protein 5 genes.Dev Psychopathol. 2014 Aug;26(3):831-49. doi: 10.1017/S095457941400042X. Dev Psychopathol. 2014. PMID: 25047302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackerman PL, Heggestad ED. Intelligence, personality, and interests: Evidence for overlapping traits. Psychological Bulletin. 1997;121:219–245. - PubMed
-
- Aluja A, Garica O, Garcia LF. Relationships among extraversion, openness to experience, and sensation seeking. Personality and Individual Differences. 2003;35:671–680.
-
- Arnsten AFT, Robbins TW. Neurochemical modulation of prefrontal cortical function. In: Stuss DT, Knight RT, editors. Principles of frontal lobe function. New York: Oxford University Press; 2002. pp. 51–84.
-
- Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HMM. Modulation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1995;65:1157–1165. - PubMed
-
- Barnett D, Manly JT, Cicchetti D. Defining child maltreatment: The interface between policy and research. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL, editors. Child abuse, child development, and social policy. Norwood, NJ: Ablex; 1993. pp. 7–73.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
