Intrathecal sufentanil versus fentanyl for lower limb surgeries - a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21804710
- PMCID: PMC3146162
Intrathecal sufentanil versus fentanyl for lower limb surgeries - a randomized controlled trial
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Intrathecal sufentanil versus fentanyl for lower limb surgeries: A randomized controlled trial.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jan-Mar;32(1):133. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.175731. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27006570 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: To compare the efficacy and safety of intrathecal sufentanil or fentanyl as adjuvants to hyperbaric bupivacaine in patients undergoing major orthopaedic lower limb surgeries in terms of onset and duration of sensory block, motor block and post-operative pain relief. PATIENTS #ENTITYSTARTX00026;
Methods: Ninety patients were recruited in this Prospective, randomized double blind study to receive either intrathecal sufentanil 5 μg (Group S), fentanyl 25 μg (Group F) or normal saline 0.5 ml (Group C) as adjuvants to 15 mg of 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine. The onset and duration of sensory and motor block were assessed intraoperatively. The pain scores were assessed postoperatively. Duration of complete and effective analgesia was recorded. The incidence of side effects such as nausea, vomiting, pruritus, shivering and PDPH was recorded.
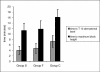
Results: The Demographic data, hemodynamic and respiratory parameters were comparable in the three groups. There was a significantly earlier onset and prolonged duration of sensory block in the sufentanil and fentanyl groups. The duration of complete and effective analgesia were also significantly prolonged in the fentanyl and sufentanil groups. Pruritus was noticed in the study groups (Groups S&F).
Conclusions: Intrathecal sufentanil (5 μg) and fentanyl (25 μg), as adjuvants lead to an earlier onset and prolonged duration of sensory block. The duration of effective analgesia with intrathecal sufentanil and fentanyl as adjuvants to hyperbaric bupivacaine is longer than that of bupivacaine alone.
Keywords: Intrathecal adjuvant, Fentanyl; Sufentanil, Lower limb surgeries.
Figures





References
-
- Wang C, Chakrabarti MK, Whitwam JG. Specific enhancement by fentanyl of the effects of intrathecal bupivacaine on nociceptive afferent but not on sympathetic efferent pathways in dogs. Anesthesiology. 1993;79:766–773. - PubMed
-
- Hunt CO, Naulty JS, Barder AM. Preoperative analgesia with subarachanoid fentanyl: bupivacaine for cesarean delivery. Anesthesiology. 1989;71:335–540. - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson L, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z. Spinal opioid analgesia a critical update. Drugs. 1988;35:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Wang JK, Nauss LA, Thomas JE. Pain relief by intrathecally applied morphine in man. Anesthesiology. 1979;50:149–151. - PubMed
-
- Leyson JE, Gommeren W, Niemegeers CJE. H-Sufentanil, a superior ligand for mu opioid receptors: binding properties and redistribution in rat brain and spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983;87:209–225. - PubMed

