Randomized double-blind comparison of ketamine-propofol and fentanyl-propofol for the insertion of laryngeal mask airway in children
- PMID: 21804715
- PMCID: PMC3146167
Randomized double-blind comparison of ketamine-propofol and fentanyl-propofol for the insertion of laryngeal mask airway in children
Abstract
Background: Till date, different combinations of adjuncts with induction agents have been tried for Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) insertion; yet, the ideal combination that provides the best insertion conditions with minimal side effects has not been identified, particularly in children. PATIENTS #ENTITYSTARTX00026;
Methods: Hundred paediatric ASA grade I and II patients, aged 3-12 years, were randomly allocated to receive intravenously either fentanyl 2μg kg(-1) (Group F, n=50) or ketamine 0.5 mg kg(-1) (Group K, n=50), before induction of anaesthesia with propofol 3.5 mg kg(-1). Arterial blood pressure and heart rate were measured before induction (baseline), immediately before induction, immediately before LMA insertion, and at 1, 3 and 5 minutes after LMA insertion. Following LMA insertion, the following six subjective endpoints were graded by a blinded anaesthetist using ordinal scales graded 1 to 3: mouth opening, gagging, swallowing, head and limb movements, laryngospasm and resistance to insertion. Duration and incidence of apnoea was also recorded.
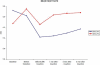
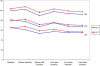
Results: The incidence of resistance to mouth opening, resistance to LMA insertion and incidence of swallowing was not statistically significant between the two groups. Coughing/ gagging was seen in 8% patients in group K as compared to 28% patients in group K. Limb/ head movements were observed in 64% patients in the fentanyl group and in 76% patients in the ketamine group. Laryngospasm was not seen in any patient in either group. Incidence of apnoea was 80% in the fentanyl group and 50% in the ketamine group. The heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure were consistently higher in the ketamine group as compared to the fentanyl group.
Conclusion: The combination of fentanyl (2μg kg-1) and propofol (3.5mg kg-1) provides better conditions for LMA insertion in children than a combination of ketamine (0.5 mg kg-1) and propofol (3.5mg kg-1).
Keywords: Fentanyl: blood pressure; Ketamine: Propofol; heart rate; laryngeal mask airway insertion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized double-blind comparison of ketamine-propofol, fentanyl-propofol and propofol-saline on haemodynamics and laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions.Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005 Apr;33(2):223-8. doi: 10.1177/0310057X0503300211. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005. PMID: 15960405 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative study of haemodynamic effects of intravenous ketamine-fentanyl and propofol-fentanyl for laryngeal mask airway insertions in children undergoing herniotomy under general anaesthesia in a nigerian tertiary hospital.Niger Postgrad Med J. 2022 Jan-Mar;29(1):36-42. doi: 10.4103/npmj.npmj_753_21. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2022. PMID: 35102948 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of addition of ketamine, fentanyl and saline with Propofol induction on hemodynamics and laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions in oral clonidine premedicated children.Saudi J Anaesth. 2012 Apr;6(2):140-4. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.97027. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 22754440 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of ketamine - propofol, fentanyl - propofol and butorphanol-propofol on haemodynamics and laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Jan;27(1):74-8. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21804711 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of ketamine and lidocaine spray with propofol for the insertion of laryngeal mask airway in children: a double-blinded randomized trial.Anesth Analg. 2002 Dec;95(6):1586-9, table of contents. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200212000-00021. Anesth Analg. 2002. PMID: 12456421 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effect of ketofol versus propofol as an induction agent on ease of laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions and hemodynamic stability in pediatrics: an observational prospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Mar 20;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0711-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 30894140 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Dexmedetomidine with Midazolam as an adjuvant with Propofol for insertion of ProSeal laryngeal mask airway in Children.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2023 Apr;51(2):128-134. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2023.21428. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2023. PMID: 37140578 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Dosages of Ketamine in Preventing Fentanyl-Induced Coughs in Children.Adv Biomed Res. 2021 Jul 29;10:20. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_218_20. eCollection 2021. Adv Biomed Res. 2021. PMID: 34476228 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the ED50 of Ciprofol Combined With or Without Fentanyl for Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion in Children: A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label, Dose-Response Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Oct 5;18:4471-4480. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S466603. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39391355 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Propofol and Ketamine-Propofol Mixture (Ketofol) on Laryngeal Tube-Suction II Conditions and Hemodynamics: A Randomized, Prospective, Double-Blind Trial.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2013 Dec;75:39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2013.06.003. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2013. PMID: 24465041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brain AIJ, Mc Ghee TD, Mc Ateer EJ, Thomas A, Abu-Saad MAW, Bushman JA. The laryngeal mask airway. Development and preliminary trials of a new type of airway. Anaesthesiay. 1985;40:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Brimacombe J, Berry AM. The laryngeal mask airway-anatomical and physiological implications. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1996;40:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Brown GW, Patel N, Ellis FR. Comparison of propofol and thiopentone for laryngeal mask insertion. Anaesthesia. 1991;46:771–772. - PubMed
-
- Scanlon P, Carey M, Power M, Kirby F. Patient response to laryngeal mask insertion after induction of anaesthesia with propofol or thiopentone. Can J Anaesth. 1993;40:816–818. - PubMed
-
- Bahk JH, Han SM, Kim SD. Management of paediatric difficult airway with a laryngeal mask airway under propofol anaesthesia. Paed Anaesth. 1999;9:163–166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical