Analgesic properties of a dexmedetomidine infusion after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 21804794
- PMCID: PMC3139306
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.82782
Analgesic properties of a dexmedetomidine infusion after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Analgesic properties of dexmedetomidine infusion after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.Saudi J Anaesth. 2020 Jan-Mar;14(1):144. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.275094. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Saudi J Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 31998047 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine is an alpha(2) -adrenergic agonist with sedative and analgesic properties. This study aimed to investigate if the use of a continuous dexmedetomidine infusion with i.v. morphine patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) could improve postoperative analgesia while reducing opioid consumption and opioid-related side effects.
Methods: In this prospective randomized, double-blinded, controlled study, 39 patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome undergoing uvulopalatopharyngoplasty were assigned to two groups. Group D (dexmedetomidine group) received a loading dose of dexmedetomidine 1 μg.kg(-1) i.v., 30 minutes before the anticipated end of surgery, followed by infusion at 0.6 μg.kg(-1) h(-1) for 24 hours. Group P (placebo group) received a bolus and infusion of placebo. In both groups, postoperative pain was initially controlled by i.v. morphine titration and then PCA with morphine. Cumulative PCA morphine consumption, pain intensities, sedation scores, cardiovascular and respiratory variables and opioid-related adverse effects were recorded for 48 hours after operation.
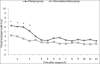
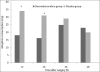
Results: Compared with placebo group, patients in the dexmedetomidine group required 52.7% less PCA morphine during the first 24 hours postoperatively, with significantly better visual analogue scale scores, less incidence of respiratory obstruction (5 vs. 12 patients, respectively; P = .037) and longer time to first analgesic request (21 (11) vs. 9 (4) minutes; P = .002). Fewer patients in group D experienced nausea and vomiting than those in group P (7 vs. 24 patients, respectively; P < .05).
Conclusion: Continuous dexmedetomidine infusion may be a useful analgesic adjuvant for patients susceptible to opioid-induced respiratory depression.
Keywords: Analgesics; dexmedetomidine; otolaryngological; pharmacology; postoperative; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ydens L, Yu S. Practice guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A report by the American society of Anesthiologists task force on perioperative management of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:1081–93. - PubMed
-
- Kim JA, Lee JJ. Preoperative predictors of difficult intubation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Can J Anaesth. 2006;53:393–7. - PubMed
-
- Zodpe P, Cho JG, Kang HJ, Hwang SJ, Lee H. Efficacy of sucralfate in the postoperative management of uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: A double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Arch otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132:182–5. - PubMed
-
- Lundkvist K, Januszkiewicz A, Friberg D. Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in 158 OSAS patients falling non-surgical treatment. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009;29:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Nikanne E, Virtmaniemi J, Aho M, Kokki H. Ketoprofen for post operative pain after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty and tonsillectomy: Two week follow up study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129:577–81. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

