Apoptosis Induction in Primary Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines and Retarded Tumor Growth in SCID Mice by Sulforaphane
- PMID: 21804859
- PMCID: PMC3139908
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/415231
Apoptosis Induction in Primary Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines and Retarded Tumor Growth in SCID Mice by Sulforaphane
Abstract
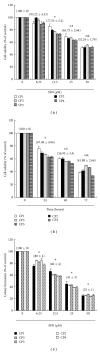
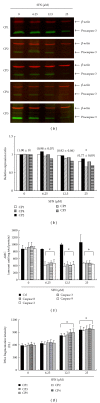
We have investigated the anticancer effects of the dietary isothiocyanate sulforaphane (SFN) on colorectal cancer (CRC), using primary cancer cells lines isolated from five Taiwanese colorectal cancer patients as the model for colorectal cancer. SFN-treated cells accumulated in metaphase (SFN 6.25 μM) and subG1 (SFN 12.5 and 25 μM) as determined by flow cytometry. In addition, treated cells showed nuclear apoptotic morphology that coincided with an activation of caspase-3, and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). Incubations at higher SFN doses (12.5 and 25 μM) resulted in cleavage of procaspase-3 and elevated caspase-2, -3, -8, and -9 activity, suggesting that the induction of apoptosis and the sulforaphane-induced mitosis delay at the lower dose are independently regulated. Daily SFN s.c. injections (400 micromol/kg/d for 3 weeks) in severe combined immunodeficient mice with primary human CRC (CP1 to CP5) s.c. tumors resulted in a decrease of mean tumor weight by 70% compared with vehicle-treated controls. Our findings suggest that, in addition to the known effects on cancer prevention, sulforaphane may have antitumor activity in established colorectal cancer.
Figures





References
-
- Mukherjee S, Bhattacharya RK, Roy M. Targeting protein kinase C (PKC) and telomerase by phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) sensitizes PC-3 cells towards chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis. Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology. 2009;28(4):269–282. - PubMed
-
- Šmerák P, Polívková Z, Štĕtina R, Bártová J, Bárta I. Antimutagenic effect of phenethyl isothiocyanate. Central European Journal of Public Health. 2009;17(2):86–92. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda T, Maruyama T, Iizuka H, et al. Phthalate esters reveal skin-sensitizing activity of phenethyl isothiocyanate in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010;48(6):1704–1708. - PubMed
-
- Liu T-T, Yang T-S. Stability and antimicrobial activity of allyl isothiocyanate during long-term storage in an oil-in-water emulsion. Journal of Food Science. 2010;75(5):C445–C451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

