CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein
- PMID: 21805345
- PMCID: PMC3651699
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0778-3
CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein
Abstract
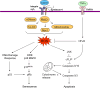
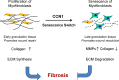
CCN1 (CYR61) is a dynamically expressed, multifunctional matricellular protein that plays essential roles in cardiovascular development during embryogenesis, and regulates inflammation, wound healing and fibrogenesis in the adult. Aberrant CCN1 expression is associated with myriad pathologies, including various cancers and diseases associated with chronic inflammation. CCN1 promotes diverse and sometimes opposing cellular responses, which can be ascribed, as least in part, to disparate activities mediated through its direct binding to distinct integrins in different cell types and contexts. Accordingly, CCN1 promotes cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis by binding to integrin α(v)β(3), and induces apoptosis and senescence through integrin α(6)β(1) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. The ability of CCN1 to trigger the accumulation of a robust and sustained level of reactive oxygen species underlies some of its unique activities as a matrix cell-adhesion molecule. Emerging studies suggest that CCN1 might be useful as a biomarker or therapeutic target in certain diseases.
© Springer Basel AG 2011
Figures

References
-
- Kyriakides TR, Bornstein P. Matricellular proteins as modulators of wound healing and the foreign body response. Thromb Haemost. 2003;90:986–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

