Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation via a Mas receptor-dependent pathway
- PMID: 21806601
- PMCID: PMC3372724
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01613.x
Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation via a Mas receptor-dependent pathway
Abstract
Background and purpose: The transactivation of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor appears to be an important central transduction mechanism in mediating diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction. Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] via its Mas receptor can prevent the development of hyperglycaemia-induced cardiovascular complications. Here, we investigated whether Ang-(1-7) can inhibit hyperglycaemia-induced EGF receptor transactivation and its classical signalling via ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK in vivo and in vitro.
Experimental approach: Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats were chronically treated with Ang-(1-7) or AG1478, a selective EGF receptor inhibitor, for 4 weeks and mechanistic studies performed in the isolated mesenteric vasculature bed as well as in primary cultures of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
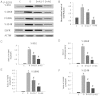
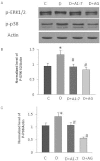
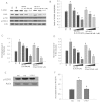
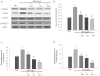
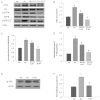
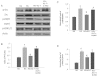
Key results: Diabetes significantly enhanced phosphorylation of EGF receptor at tyrosine residues Y992, Y1068, Y1086, Y1148, as well as ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK in the mesenteric vasculature bed whereas these changes were significantly attenuated upon Ang-(1-7) or AG1478 treatment. In VSMCs grown in conditions of high glucose (25 mM), an Src-dependent elevation in EGF receptor phosphorylation was observed. Ang-(1-7) inhibited both Ang II- and glucose-induced transactivation of EGF receptor. The inhibition of high glucose-mediated Src-dependant transactivation of EGF receptor by Ang-(1-7) could be prevented by a selective Mas receptor antagonist, D-Pro7-Ang-(1-7).
Conclusions and implications: These results show for the first time that Ang-(1-7) inhibits EGF receptor transactivation via a Mas receptor/Src-dependent pathway and might represent a novel general mechanism by which Ang-(1-7) exerts its beneficial effects in many disease states including diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Almendro V, García-Recio S, Gascón P. Tyrosine kinase receptor transactivation associated to G protein-coupled receptors. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11:1169–1180. - PubMed
-
- Andrew A, Kathryn JW, Alison JC, Yuan Z, Richard EG, Darren JK. Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor preserves podocytes and attenuates albuminuria in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 2011;16:573–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

