Improving adherence with amlodipine/atorvastatin therapy: IMPACT study
- PMID: 21806770
- PMCID: PMC8108855
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00478.x
Improving adherence with amlodipine/atorvastatin therapy: IMPACT study
Erratum in
- J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011 Oct;13(10):784. Nesbitt, Shawna [added]
Abstract
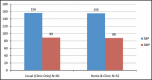
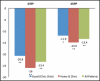
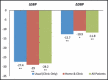
Hypertension is prevalent in the United States and remains uncontrolled. The primary objective of the study was to determine the effect of once-daily dosing of a combination therapy for blood pressure (BP) and dyslipidemia using home BP monitoring on reaching clinical BP and the effect of daily dosing of combination therapy on reaching lipid goals. The study was conducted in middle-aged, indigent, African Americans who had high-risk, resistant hypertension and dyslipidemia. Patients were randomly assigned to either the home and clinic BP group or usual care group and were followed for 6 months. The average BPs for each group were compared and used to titrate the study drug appropriately. Both groups achieved significant declines in BP, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (P<.0001). These findings demonstrate that BP control could be achieved at a rate of 43.5% compared with the 2004 national control rate of 35%. The LDL control rate was also improved. Cardiovascular risk reduction has been proven to be achieved through managing lipids and BP. This trial demonstrates that these goals can be achieved similar to other groups in indigent African Americans with high-risk hypertension and dyslipidemia.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Chun‐Ju H, Donald C, Beatty P, et al. National health statistics reports. National ambulatory medical care survey 2007. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr003.pdf. Number 27. Accessed November 3, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2008 update. A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–e146. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen N, Magno C, Hinojosa M, et al. Association of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome with obesity: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999 to 2004. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207(6):928–934. - PubMed
-
- Johnson M, Pietz D, Battleman D, et al. Prevalence of comorbid hypertension and dyslipidemia and associated cardiovascular disease. Am J Manag Care. 2004;10:926–932. - PubMed
-
- Borghi C. Interactions between hypercholesterolemia and hypertension: implications for therapy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002;11:489–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

