High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 21806788
- PMCID: PMC3163635
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-4-31
High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The purpose of the study was to investigate the expression and prognostic value of STAT3 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Methods: Seventy-four DLBCL patients from 2001 to 2007 were reviewed in the study. The STAT3 expression in their tumor tissues was examined using the immunohistochemistry (IHC) method, and evaluated for its association with clinicopathological parameters.
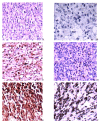
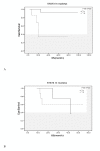
Results: Strong nuclear staining of STAT3 and phosphorylated-STAT3tyr705 (P-STAT3) were observed in 19 cases (25.7%) and 24 cases (32.4%), respectively, and the expression levels were highly consistent between them (P = 0.001). The high nuclear expression of STAT3 was more frequent in the non-germinal center B cell-like (non-GCB) DLBCL than that in the GCB subtype, but not reaching significance (P < 0.061). The high nuclear expression of STAT3 was found to be correlated with poor overall survival (OS) (P = 0.005). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that the STAT3 expression was an independent prognostic factor for DLBCL patients regardless of CHOP or R-CHOP regimen used as the first-line therapy.
Conclusion: STAT3 is more frequently expressed in non-GCB DLBCL than that in GCB subtype, and its strong nuclear expression is correlated with poor OS in DLBCL.
Figures

References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW, (Eds) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, IARC Press, Lyon; 2008.
-
- Harris N L, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JK, Cleary ML, Delsol G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Falini B, Gatter KC. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994;84(5):1361–1392. - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109(5):1857–1861. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-038257. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh A A, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–11. doi: 10.1038/35000501. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

