The immunological potency and therapeutic potential of a prototype dual vaccine against influenza and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21806809
- PMCID: PMC3162512
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-127
The immunological potency and therapeutic potential of a prototype dual vaccine against influenza and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Numerous pre-clinical studies and clinical trials demonstrated that induction of antibodies to the β-amyloid peptide of 42 residues (Aβ42) elicits therapeutic effects in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, an active vaccination strategy based on full length Aβ42 is currently hampered by elicitation of T cell pathological autoreactivity. We attempt to improve vaccine efficacy by creating a novel chimeric flu vaccine expressing the small immunodominant B cell epitope of Aβ42. We hypothesized that in elderly people with pre-existing memory Th cells specific to influenza this dual vaccine will simultaneously boost anti-influenza immunity and induce production of therapeutically active anti-Aβ antibodies.
Methods: Plasmid-based reverse genetics system was used for the rescue of recombinant influenza virus containing immunodominant B cell epitopes of Aβ42 (Aβ1-7/10).
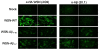
Results: Two chimeric flu viruses expressing either 7 or 10 aa of Aβ42 (flu-Aβ1-7 or flu-Aβ1-10) were generated and tested in mice as conventional inactivated vaccines. We demonstrated that this dual vaccine induced therapeutically potent anti-Aβ antibodies and anti-influenza antibodies in mice.
Conclusion: We suggest that this strategy might be beneficial for treatment of AD patients as well as for prevention of development of AD pathology in pre-symptomatic individuals while concurrently boosting immunity against influenza.
Figures


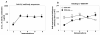



References
-
- Price DL, Sisodia SS. Cellular and molecular biology of Alzheimer's disease and animal models. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:435–446. - PubMed
-
- Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K. et al.Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse [see comments] Nature. 1999;400:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Morgan D, Diamond DM, Gottschall PE, Ugen KE, Dickey C, Hardy J, Duff K, Jantzen P, DiCarlo G, Wilcock D. et al.A beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2000;408:982–985. - PubMed
-
- Janus C, Pearson J, McLaurin J, Mathews PM, Jiang Y, Schmidt SD, Chishti MA, Horne P, Heslin D, French J. et al.A beta peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2000;408:979–982. - PubMed
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K. et al.Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

