The human sirtuin family: evolutionary divergences and functions
- PMID: 21807603
- PMCID: PMC3230576
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-5-5-485
The human sirtuin family: evolutionary divergences and functions
Abstract
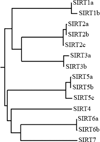
The sirtuin family of proteins is categorised as class III histone deacetylases that play complex and important roles in ageing-related pathological conditions such as cancer and the deregulation of metabolism. There are seven members in humans, divided into four classes, and evolutionarily conserved orthologues can be found in most forms of life, including both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The highly conserved catalytic core domain composed of a large oxidised nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-binding Rossmann fold subunit suggests that these proteins belong to a family of nutrient-sensing regulators. Along with their function in regulating cellular metabolism in response to stressful conditions, they are implicated in modifying a wide variety of substrates; this increases the complexity of unravelling the interplay of sirtuins and their partners. Over the past few years, all of these new findings have attracted the interest of researchers exploring potential therapeutic implications related to the function of sirtuins. It remains to be elucidated whether, indeed, sirtuins can serve as molecular targets for the treatment of human illnesses.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous