Phylogenetic structure of mammal assemblages at large geographical scales: linking phylogenetic community ecology with macroecology
- PMID: 21807735
- PMCID: PMC3138611
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0021
Phylogenetic structure of mammal assemblages at large geographical scales: linking phylogenetic community ecology with macroecology
Abstract
Phylogenetic community ecology seeks to explain the processes involved in the formation of species assemblages by analysing their phylogenetic structure, and to date has focused primarily on local-scale communities. Macroecology, on the other hand, is concerned with the structure of assemblages at large geographical scales, but has remained largely non-phylogenetic. Analysing the phylogenetic structure of large-scale assemblages provides a link between these two research programmes. In this paper, I ask whether we should expect large-scale assemblages to show significant phylogenetic structure, by outlining some of the ecological and macroevolutionary processes that may play a role in assemblage formation. As a case study, I then explore the phylogenetic structure of carnivore assemblages within the terrestrial ecoregions of Africa. Many assemblages at these scales are indeed phylogenetically non-random (either clustered or overdispersed). One interpretation of the observed patterns of phylogenetic structure is that many clades underwent rapid biome-filling radiations, followed by diversification slowdown and competitive sorting as niche space became saturated.
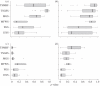
Figures


References
-
- Webb C. O. 2000. Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: an example for rain forest trees. Am. Nat. 156, 145–155 10.1086/303378 (doi:10.1086/303378) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emerson B. C., Gillespie R. G. 2008. Phylogenetic analysis of community assembly and structure over space and time. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23, 619–630 10.1016/j.tree.2008.07.005 (doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.07.005) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vamosi S. M., Heard S. B., Vamosi J. C., Webb C. O. 2009. Emerging patterns in the comparative analysis of phylogenetic community structure. Mol. Ecol. 18, 572–592 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04001.x (doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04001.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Webb C. O. 2006. Integrating phylogenies into community ecology. Ecology 87, S1–S2 10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1:IPICE]2.0.CO;2 (doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1:IPICE]2.0.CO;2) - DOI
-
- Webb C. O., Ackerly D. D., McPeek M. A., Donoghue M. J. 2002. Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 33, 475–505 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150448 (doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150448) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
