RSC facilitates Rad59-dependent homologous recombination between sister chromatids by promoting cohesin loading at DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 21807899
- PMCID: PMC3187356
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01269-10
RSC facilitates Rad59-dependent homologous recombination between sister chromatids by promoting cohesin loading at DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
Homologous recombination repairs DNA double-strand breaks by searching for, invading, and copying information from a homologous template, typically the homologous chromosome or sister chromatid. Tight wrapping of DNA around histone octamers, however, impedes access of repair proteins to DNA damage. To facilitate DNA repair, modifications of histones and energy-dependent remodeling of chromatin are required, but the precise mechanisms by which chromatin modification and remodeling enzymes contribute to homologous DNA repair are unknown. Here we have systematically assessed the role of budding yeast RSC (remodel structure of chromatin), an abundant, ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complex, in the cellular response to spontaneous and induced DNA damage. RSC physically interacts with the recombination protein Rad59 and functions in homologous recombination. Multiple recombination assays revealed that RSC is uniquely required for recombination between sister chromatids by virtue of its ability to recruit cohesin at DNA breaks and thereby promoting sister chromatid cohesion. This study provides molecular insights into how chromatin remodeling contributes to DNA repair and maintenance of chromatin fidelity in the face of DNA damage.
Figures
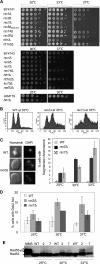

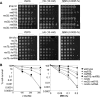
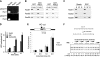
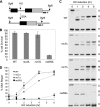

Comment in
-
Roles of RSC, Rad59, and cohesin in double-strand break repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;31(19):3921-3. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05974-11. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21844225 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bai Y., Symington L. S. 1996. A Rad52 homolog is required for RAD51-independent mitotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 10:2025–2037 - PubMed
-
- Bao Y., Shen X. 2007. Chromatin remodeling in DNA double-strand break repair. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 17:126–131 - PubMed
-
- Cairns B. R., et al. 1996. RSC, an essential, abundant chromatin-remodeling complex. Cell 87:1249–1260 - PubMed
-
- Cairns B. R., et al. 1999. Two functionally distinct forms of the RSC nucleosome-remodeling complex, containing essential AT hook, BAH, and bromodomains. Mol. Cell 4:715–723 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
