Analysis of protein dynamics within the septate junction reveals a highly stable core protein complex that does not include the basolateral polarity protein Discs large
- PMID: 21807950
- PMCID: PMC3148133
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.087700
Analysis of protein dynamics within the septate junction reveals a highly stable core protein complex that does not include the basolateral polarity protein Discs large
Abstract
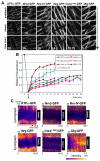
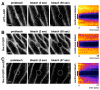
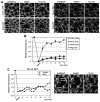
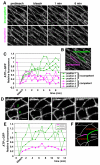
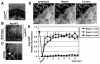
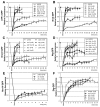
Barrier junctions prevent pathogen invasion and restrict paracellular leakage across epithelial sheets. To understand how one barrier junction, the septate junction (SJ), is regulated in vivo, we used fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) to examine SJ protein dynamics in Drosophila. Most SJ-associated proteins, including Coracle, Neurexin IV and Nervana 2, displayed similar, extremely immobile kinetics. Loss of any of these components resulted in dramatically increased mobility of all others, suggesting that they form a single, highly interdependent core complex. Immobilization of SJ core components coincided with formation of the morphological SJ but occurred after their known role in maintaining epithelial polarity, suggesting that these functions are independent. In striking contrast to the core components, the tumor suppressor protein Discs large was much more mobile and its loss did not affect mobility of core SJ proteins, suggesting that it is not a member of this complex, even though it colocalizes with the SJ. Similarly, disruption of endocytosis affected localization of SJ core components, but did not affect their mobility. These results indicate that formation of a stable SJ core complex is separable from its proper subcellular localization, and provide new insights into the complex processes that regulate epithelial polarity and assembly of the SJ.
© 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd
Figures


References
-
- Baumgartner S., Littleton J. T., Broadie K., Bhat M. A., Harbecke R., Lengyel J. A., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Prokop A., Bellen H. J. (1996). A Drosophila neurexin is required for septate junction and blood-nerve barrier formation and function. Cell 87, 1059-1068 - PubMed
-
- Behr M., Riedel D., Schuh R. (2003). The claudin-like megatrachea is essential in septate junctions for the epithelial barrier function in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 5, 611-620 - PubMed
-
- Bhat M. A., Rios J. C., Lu Y., Garcia-Fresco G. P., Ching W., St Martin M., Li J., Einheber S., Chesler M., Rosenbluth J., et al. (2001). Axon-glia interactions and the domain organization of myelinated axons requires neurexin IV/Caspr/Paranodin. Neuron 30, 369-383 - PubMed
-
- Bilder D., Perrimon N. (2000). Localization of apical epithelial determinants by the basolateral PDZ protein Scribble. Nature 403, 676-680 - PubMed
-
- Bilder D., Li M., Perrimon N. (2000). Cooperative regulation of cell polarity and growth by Drosophila tumor suppressors. Science 289, 113-116 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

