OmpK26, a novel porin associated with carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 21807980
- PMCID: PMC3186958
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00309-11
OmpK26, a novel porin associated with carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
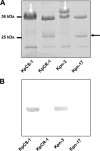
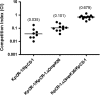
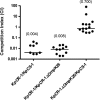
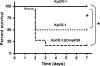
Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to carbapenems are being isolated with increasing frequency. Loss of the expression of the major nonspecific porins OmpK35/36 is a frequent feature in these isolates. In this study, we looked for porins that could compensate for the loss of the major porins in carbapenem-resistant organisms. Comparison of the outer membrane proteins from two K. pneumoniae clinical isogenic isolates that are susceptible (KpCS-1) and resistant (KpCR-1) to carbapenems revealed the absence of OmpK35/36 and the presence of a new 26-kDa protein in the resistant isolate. An identical result was obtained when another pair of isogenic isolates that are homoresistant (Kpn-3) and heteroresistant (Kpn-17) to carbapenems were compared. Mass spectrometry and DNA sequencing analysis demonstrated that this new protein, designated OmpK26, is a small monomeric oligogalacturonate-specific porin that belongs to the KdgM family of porins. Insertion-duplication mutagenesis of the OmpK26 coding gene, yjhA, in the carbapenem-resistant, porin-deficient isolate KpCR-1 caused the expression of OmpK36 and the reversion to the carbapenem-susceptible phenotype, suggesting that OmpK26 is indispensable for KpCR-1 to lose OmpK36 and become resistant to these antibiotics. Moreover, loss of the major porin and expression of OmpK26 reduced in vitro fitness and attenuated virulence in a murine model of acute systemic infection. Altogether, these results indicate that expression of the oligogalacturonate-specific porin OmpK26 compensates for the absence of OmpK35/36 and allows carbapenem resistance in K. pneumoniae but cannot restore the fitness of the microorganism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay between porin deficiency, fitness, and virulence in carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Feb 7;21(2):e1012902. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012902. eCollection 2025 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39919103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Trends in Proteome Remodeling of the Outer Membrane Modulate Antimicrobial Permeability in Klebsiella pneumoniae.mBio. 2020 Apr 14;11(2):e00603-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00603-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32291303 Free PMC article.
-
Role of association of OmpK35 and OmpK36 alteration and blaESBL and/or blaAmpC genes in conferring carbapenem resistance among non-carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Dec;52(6):898-905. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29621592
-
Role of Klebsiella pneumoniae LamB Porin in antimicrobial resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Apr;55(4):1803-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01441-10. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21282437 Free PMC article.
-
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and the permeability barrier.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008 Jan;14 Suppl 1:82-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01860.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008. PMID: 18154531 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of OmpR in the Expression of Genes of the KdgR Regulon Involved in the Uptake and Depolymerization of Oligogalacturonides in Yersinia enterocolitica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Aug 15;7:366. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00366. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28861396 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2017 Mar 29;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12941-017-0191-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2017. PMID: 28356109 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in virulence of pneumolysin and autolysin mutants constructed by insertion duplication mutagenesis and in-frame deletion in Streptococcus pneumoniae.BMC Biotechnol. 2014 Feb 21;14:16. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-16. BMC Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24558977 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and analysis of different interactions between resistance mechanisms and carbapenems in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Braz J Microbiol. 2017 Jul-Sep;48(3):493-498. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Braz J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28291698 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between porin deficiency, fitness, and virulence in carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Feb 7;21(2):e1012902. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012902. eCollection 2025 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39919103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ausubel F. M., et al. 1997. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley Interscience, New York, NY
-
- Blot N., Berrier C., Hugouvieux-Cottet-Pattat N., Ghazi A., Condemine G. 2002. The oligogalacturonate-specific porin KdgM of Erwinia chrysanthemi belongs to a new porin family. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7936–7944 - PubMed
-
- Cabezón V., Llama-Palacios A., Nombela C., Monteoliva L., Gil C. 2009. Analysis of Candida albicans plasma membrane proteome. Proteomics 9:4770–4786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

