The RNA-binding protein Rrm4 is essential for efficient secretion of endochitinase Cts1
- PMID: 21808052
- PMCID: PMC3237082
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.011213
The RNA-binding protein Rrm4 is essential for efficient secretion of endochitinase Cts1
Abstract
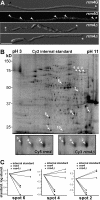
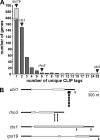
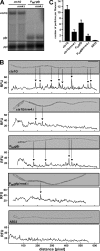
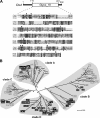
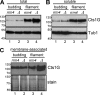
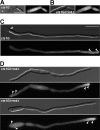
Long-distance transport of mRNAs is crucial in determining spatio-temporal gene expression in eukaryotes. The RNA-binding protein Rrm4 constitutes a key component of microtubule-dependent mRNA transport in filaments of Ustilago maydis. Although a number of potential target mRNAs could be identified, cellular processes that depend on Rrm4-mediated transport remain largely unknown. Here, we used differential proteomics to show that ribosomal, mitochondrial, and cell wall-remodeling proteins, including the bacterial-type endochitinase Cts1, are differentially regulated in rrm4Δ filaments. In vivo UV crosslinking and immunoprecipitation and fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed that cts1 mRNA represents a direct target of Rrm4. Filaments of cts1Δ mutants aggregate in liquid culture suggesting an altered cell surface. In wild type cells Cts1 localizes predominantly at the growth cone, whereas it accumulates at both poles in rrm4Δ filaments. The endochitinase is secreted and associates most likely with the cell wall of filaments. Secretion is drastically impaired in filaments lacking Rrm4 or conventional kinesin Kin1 as well as in filaments with disrupted microtubules. Thus, Rrm4-mediated mRNA transport appears to be essential for efficient export of active Cts1, uncovering a novel molecular link between mRNA transport and the mechanism of secretion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The RNA-binding protein Rrm4 is essential for polarity in Ustilago maydis and shuttles along microtubules.J Cell Sci. 2006 Dec 1;119(Pt 23):4964-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03287. Epub 2006 Nov 14. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 17105762
-
The fungal RNA-binding protein Rrm4 mediates long-distance transport of ubi1 and rho3 mRNAs.EMBO J. 2009 Jul 8;28(13):1855-66. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.145. Epub 2009 Jun 4. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19494833 Free PMC article.
-
Applying unconventional secretion of the endochitinase Cts1 to export heterologous proteins in Ustilago maydis.J Biotechnol. 2012 Oct 15;161(2):80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 16. J Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22446315
-
Posttranscriptional control of growth and development in Ustilago maydis.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Dec;13(6):693-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.08.013. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20880737 Review.
-
Microtubule-dependent mRNA transport in fungi.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Jul;9(7):982-90. doi: 10.1128/EC.00030-10. Epub 2010 May 14. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20472693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurospora crassa NKIN2, a kinesin-3 motor, transports early endosomes and is required for polarized growth.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 Jul;12(7):1020-32. doi: 10.1128/EC.00081-13. Epub 2013 May 17. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23687116 Free PMC article.
-
A FYVE zinc finger domain protein specifically links mRNA transport to endosome trafficking.Elife. 2015 May 18;4:e06041. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06041. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25985087 Free PMC article.
-
The multi PAM2 protein Upa2 functions as novel core component of endosomal mRNA transport.EMBO Rep. 2019 Sep;20(9):e47381. doi: 10.15252/embr.201847381. Epub 2019 Jul 24. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31338952 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing a Chitinase Gene, PstChia1, Reduces Virulence of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 4;24(9):8215. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098215. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175921 Free PMC article.
-
Walking the line: mechanisms underlying directional mRNA transport and localisation in neurons and beyond.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2665-2681. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03724-3. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33341920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gierz G., Bartnicki-Garcia S. (2001) A three-dimensional model of fungal morphogenesis based on the vesicle supply center concept. J. Theor. Biol. 208, 151–164 - PubMed
-
- Fischer R., Zekert N., Takeshita N. (2008) Polarized growth in fungi - interplay between the cytoskeleton, positional markers and membrane domains. Mol. Microbiol. 68, 813–826 - PubMed
-
- Harris S. D. (2006) Cell polarity in filamentous fungi: shaping the mold. Int. Rev. Cytol. 251, 41–77 - PubMed
-
- Brefort T., Doehlemann G., Mendoza-Mendoza A., Reissmann S., Djamei A., Kahmann R. (2009) Ustilago maydis as a Pathogen. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 47, 423–445 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

