Smart Magnetically Responsive Hydrogel Nanoparticles Prepared by a Novel Aerosol-Assisted Method for Biomedical and Drug Delivery Applications
- PMID: 21808638
- PMCID: PMC3146763
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/910539
Smart Magnetically Responsive Hydrogel Nanoparticles Prepared by a Novel Aerosol-Assisted Method for Biomedical and Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
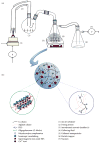
We have developed a novel spray gelation-based method to synthesize a new series of magnetically responsive hydrogel nanoparticles for biomedical and drug delivery applications. The method is based on the production of hydrogel nanoparticles from sprayed polymeric microdroplets obtained by an air-jet nebulization process that is immediately followed by gelation in a crosslinking fluid. Oligoguluronate (G-blocks) was prepared through the partial acid hydrolysis of sodium alginate. PEG-grafted chitosan was also synthesized and characterized (FTIR, EA, and DSC). Then, magnetically responsive hydrogel nanoparticles based on alginate and alginate/G-blocks were synthesized via aerosolization followed by either ionotropic gelation or both ionotropic and polyelectrolyte complexation using CaCl(2) or PEG-g-chitosan/CaCl(2) as crosslinking agents, respectively. Particle size and dynamic swelling were determined using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and microscopy. Surface morphology of the nanoparticles was examined using SEM. The distribution of magnetic cores within the hydrogels nanoparticles was also examined using TEM. In addition, the iron and calcium contents of the particles were estimated using EDS. Spherical magnetic hydrogel nanoparticles with average particle size of 811 ± 162 to 941 ± 2 nm were obtained. This study showed that the developed method is promising for the manufacture of hydrogel nanoparticles, and it represents a relatively simple and potential low-cost system.
Figures









References
-
- Qiu Y, Park K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2001;53(3):321–339. - PubMed
-
- Morales MA, Finotelli PV, Coaquira JAH, et al. In situ synthesis and magnetic studies of iron oxide nanoparticles in calcium-alginate matrix for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering C. 2008;28(2):253–257.
-
- Kim DK, Zhang Y, Kehr J, Klason T, Bjelke B, Muhammed M. Characterization and MRI study of surfactantcoated superparamagnetic nanoparticles administered into the rat brain. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 2001;225(1-2):256–261.
-
- Reynolds CH, Annan N, Beshah K, et al. Gadoliniumloaded nanoparticles: new contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2000;122(37):8940–8945.
-
- Lübbe AS, Bergemann C, Riess H, et al. Clinical experiences with magnetic drug targeting: a phase I study with 4′-epidoxorubicin in 14 patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Research. 1996;56(20):4686–4693. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
