Pelvic bone and hip joint hydatid disease revealing a retroperitoneal location
- PMID: 21808672
- PMCID: PMC3143965
- DOI: 10.4081/or.2009.e8
Pelvic bone and hip joint hydatid disease revealing a retroperitoneal location
Abstract
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease produced by the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus. Hydatid disease of bone is rarely seen in humans and it has been reported in only 1-2% of cases of echinococcosis. We present a patient who developed hydatid disease of the left pelvic and femoral bones with cartilage destruction of the ipsilateral hip joint revealing a retroperitoneal location of hydatid cyst. Hydatid bone must be present in the differential diagnosis of chronic monoarthritis. Skeletal involvement is usually secondary to visceral hydatidosis that we must research. Early diagnosis allows eradication and salvage of the bone and the hip joint. Delayed diagnosis is always fraught with the risk of recurrence and sepsis.
Keywords: hydatid bone; joint involvement; retroperitoneal hydatid cyst; surgery..
Figures
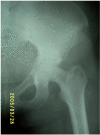

References
-
- Agarwal S, Shah A, Khadi SK, Rooney RJ. Hydatid bone disease of the pelvis: a report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Orthop. 1992;280:251–5. - PubMed
-
- Szypryt EP, Morris DL, Mulholland RC. Combined chemotherapy and surgery for hydatid bone disease. J Bone Joint Surg. 1987;69B:141–4. - PubMed
-
- Uzel M, Hiz M, Aydingoz O. Curettage, local heat and cement application in echinococcosis of bone. Presented at the Joint Meeting of EMSOS-AMSTS; Florence, Italy. 1995.
-
- Argenson C, Griffet J, Lacour C, et al. Vertebral hydatid cyst. A propos of 2 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Rep Appar Mot. 1989;75:267–70. - PubMed
-
- Porat S, Joseph KN. Hydatid disease of bone: a case report and review of the literature. Isr J Med Sci. 1978;14:223–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
