On network derivation, classification, and visualization: a response to Habeck and Moeller
- PMID: 21808745
- PMCID: PMC3146759
On network derivation, classification, and visualization: a response to Habeck and Moeller
Abstract
In the decade and a half since Biswal's fortuitous discovery of spontaneous correlations in functional imaging data, the field of functional connectivity (FC) has seen exponential growth resulting in the identification of widely-replicated intrinsic networks and the innovation of novel analytic methods with the promise of diagnostic application. As such a young field undergoing rapid change, we have yet to converge upon a desired and needed set of standards. In this issue, Habeck and Moeller begin a dialogue for developing best practices by providing four criticisms with respect to FC estimation methods, interpretation of FC networks, assessment of FC network features in classifying sub-populations, and network visualization. Here, we respond to Habeck and Moeller and provide our own perspective on the concerns raised in the hope that the neuroimaging field will benefit from this discussion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
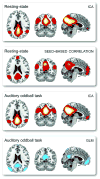
Figures


References
-
- Allen EA, Erhardt EB, Damaraju E, Gruner W, Segall JM, Silva RF, Havlicek M, Rachakonda S, Fries J, Kalyanam R, Michael AM, Caprihan A, Turner JA, Eichele T, Adelsheim S, Bryan AD, Bustillo J, Clark VP, Feldstein Ewing SW, Filbey F, Ford CC, Hutchison K, Jung RE, Kiehl KA, Kodituwakku P, Komesu YM, Mayer AR, Pearlson GD, Phillips JP, Sadek JR, Stevens M, Teuscher U, Thoma RJ, Calhoun VD. A baseline for the multivariate comparison of resting-state networks. Front Syst Neurosci. 2011:4–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N, Paradiso S, O’Leary D. “Cognitive dysmetria” as an integrative theory of schizophrenia: a dysfunction in cortical-subcortical-cerebellar circuitry? Schizophrenia Bulletin. 1998;24(2):203. - PubMed
-
- Biswal BB, Mennes M, Zuo XN, Gohel S, Kelly C, Smith SM, Beckmann CF, Adelstein JS, Buckner RL, Colcombe S, Dogonowski AM, Ernst M, Fair D, Hampson M, Hoptman MJ, Hyde JS, Kiviniemi VJ, Kotter R, Li SJ, Lin CP, Lowe MJ, Mackay C, Madden DJ, Madsen KH, Margulies DS, Mayberg HS, McMahon K, Monk CS, Mostofsky SH, Nagel BJ, Pekar JJ, Peltier SJ, Petersen SE, Riedl V, Rombouts SA, Rypma B, Schlaggar BL, Schmidt S, Seidler RD, Siegle GJ, Sorg C, Teng GJ, Veijola J, Villringer A, Walter M, Wang L, Weng XC, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Williamson P, Windischberger C, Zang YF, Zhang HY, Castellanos FX, Milham MP. Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(10):4734–4739. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
