Tumor necrosis factor inhibits mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts via the ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1
- PMID: 21809421
- PMCID: PMC3708970
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.703
Tumor necrosis factor inhibits mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts via the ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1
Abstract
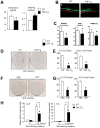
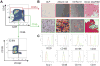
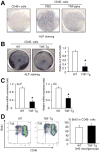
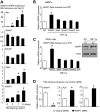
Patients with chronic inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, often have osteoporosis due to a combination of Tumor necrosis factor-induced increased bone resorption and reduced bone formation. To test if TNF inhibits bone formation by affecting the commitment and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into osteoblasts, we examined the osteogenic potential of MSCs from TNF transgenic (TNF-Tg) mice, a model of chronic inflammatory arthritis. MSC-enriched cells were isolated from bone marrow stromal cells using negative selection with anti-CD45 antibody coated magnetic beads. The expression profile of MSC surface markers the osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic properties of CD45(-) cells were confirmed by FACS and cell differentiation assays. MSC-enriched CD45(-) cells from TNF-Tg mice formed significantly decreased numbers of fibroblast and ALP(+) colonies and had a decreased expression of osteoblast marker genes. As TNF may upregulate ubiquitin ligases, which negatively regulate osteoblast differentiation, we examined the expression levels of several ubiquitin ligases and found that Wwp1 expression was significantly increased in MSC-enriched CD45(-) cells of TNF-Tg mice. Wwp1 knockdown rescued impaired osteoblast differentiation of TNF-Tg CD45(-) cells. Wwp1 promotes ubiquitination and degradation of JunB, an AP-1 transcription factor that positively regulates osteoblast differentiation. Injection of TNF into wild-type mice resulted in decreased osteoblast differentiation of MSCs and increased JunB ubiquitination, which was completely blocked in Wwp1(-/-) mice. Thus, Wwp1 targets JunB for ubiquitination and degradation in MSCs after chronic exposure to TNF, and inhibition of Wwp1 in MSCs could be a new mechanism to limit inflammation-mediated osteoporosis by promoting their differentiation into osteoblasts.
Copyright © 2011 AlphaMed Press.
Figures
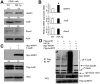
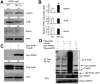
References
-
- Canalis E. Effects of tumor necrosis factor on bone formation in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987;121:1596–1604. - PubMed
-
- Li YP, Stashenko P. Proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6, but not IL-1, down-regulate the osteocalcin gene promoter. J Immunol. 1992;148:788–794. - PubMed
-
- Nanes MS. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Molecular and cellular mechanisms in skeletal pathology. Gene. 2003;321:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert L, He X, Farmer P, et al. Expression of the osteoblast differentiation factor RUNX2 (Cbfa1/AML3/Pebp2alpha A) is inhibited by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2695–2701. - PubMed
-
- Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, et al. Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med. 2007;13:156–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

