A synaptogenic amide N-docosahexaenoylethanolamide promotes hippocampal development
- PMID: 21810478
- PMCID: PMC3215906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2011.07.002
A synaptogenic amide N-docosahexaenoylethanolamide promotes hippocampal development
Abstract
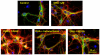
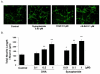
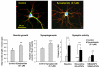
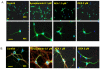
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), the n-3 essential fatty acid that is highly enriched in the brain, increases neurite growth and synaptogenesis in cultured mouse fetal hippocampal neurons. These cellular effects may underlie the DHA-induced enhancement of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory functions. We found that N-docsahexaenoylethanolamide (DEA), an ethanolamide derivative of DHA, is a potent mediator for these actions. This is supported by the observation that DHA is converted to DEA by fetal mouse hippocampal neuron cultures and a hippocampal homogenate, and DEA is present endogenously in the mouse hippocampus. Furthermore, DEA stimulates neurite growth and synaptogenesis at substantially lower concentrations than DHA, and it enhances glutamatergic synaptic activities with concomitant increases in synapsin and glutamate receptor subunit expression in the hippocampal neurons. These findings suggest that DEA, an ethanolamide derivative of DHA, is a synaptogenic factor, and therefore we suggest utilizing the term 'synaptamide'. This brief review summarizes the neuronal production and actions of synaptamide and describes other N-docosahexaenoyl amides that are present in the brain.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptamide, endocannabinoid-like derivative of docosahexaenoic acid with cannabinoid-independent function.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013 Jan;88(1):121-5. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013. PMID: 22959887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Docosahexaenoylethanolamide promotes development of hippocampal neurons.Biochem J. 2011 Apr 15;435(2):327-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20102118. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21281269 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid promotes hippocampal neuronal development and synaptic function.J Neurochem. 2009 Oct;111(2):510-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06335.x. Epub 2009 Aug 13. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19682204 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of N-Docosahexanoylethanolamine from Unesterified Docosahexaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoyl-Lysophosphatidylcholine in Neuronal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 20;21(22):8768. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228768. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233525 Free PMC article.
-
N-Docosahexaenoylethanolamine: A neurotrophic and neuroprotective metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Dec;64:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 29572109 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging class of omega-3 fatty acid endocannabinoids & their derivatives.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019 Aug;143:106337. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.106337. Epub 2019 May 11. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019. PMID: 31085370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal endocannabinoids orchestrate the organization of pancreatic islet microarchitecture.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 10;112(45):E6185-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519040112. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26494286 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Effects of N-Docosahexaenoyl Ethanolamine in Breast Cancer: Molecular and Cellular Insights.Molecules. 2023 Apr 25;28(9):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093694. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect of docosahexaenoic acid nanoemulsion on erectile function in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 14;6:33040. doi: 10.1038/srep33040. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27625175 Free PMC article.
-
The docosanoid neuroprotectin D1 induces homeostatic regulation of neuroinflammation and cell survival.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013 Jan;88(1):127-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013. PMID: 23022417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Birch EE, Garfield S, Hoffman DR, Uauy R, Birch DG. A randomized controlled trial of early dietary supply of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and mental development in term infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000;42:174–81. - PubMed
-
- Robson LG, Dyall S, Sidloff D, Michael-Titus AT. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids increase the neurite outgrowth of rat sensory neurons throughout development and in aged animals. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:678–87. - PubMed
-
- Eldho NV, Feller SE, Tristram-Nagle S, Polozov IV, Gawrisch K. Polyunsaturated docosahexaenoic vs docosapentaenoic acid differences in lipid matrix properties from the loss of one double bond. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:6409–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

