Beneficial effects of exendin-4 on experimental polyneuropathy in diabetic mice
- PMID: 21810596
- PMCID: PMC3161330
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1462
Beneficial effects of exendin-4 on experimental polyneuropathy in diabetic mice
Abstract
Objective: The therapeutic potential of exendin-4, an agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), on diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice was investigated.
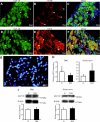
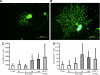
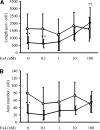
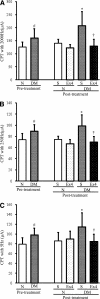
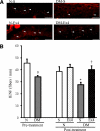
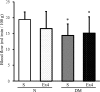
Research design and methods: The presence of the GLP-1R in lumbar dorsal root ganglion (DRG) was evaluated by immunohistochemical analyses. DRG neurons were dissected from C57BL6/J mice and cultured with or without Schwann cell-conditioned media in the presence or absence of GLP-1 (7-37) or exendin-4. Then neurite outgrowth was determined. In animal-model experiments, mice were made diabetic by STZ administration, and after 12 weeks of diabetes, exendin-4 (10 nmol/kg) was intraperitoneally administered once daily for 4 weeks. Peripheral nerve function was determined by the current perception threshold and motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity (MNCV and SNCV, respectively). Sciatic nerve blood flow (SNBF) and intraepidermal nerve fiber densities (IENFDs) also were evaluated.
Results: The expression of the GLP-1R in DRG neurons was confirmed. GLP-1 (7-37) and exendin-4 significantly promoted neurite outgrowth of DRG neurons. Both GLP-1R agonists accelerated the impaired neurite outgrowth of DRG neurons cultured with Schwann cell-conditioned media that mimicked the diabetic condition. At the doses used, exendin-4 had no effect on blood glucose or HbA(1c) levels. Hypoalgesia and delayed MNCV and SNCV in diabetic mice were improved by exendin-4 without affecting the reduced SNBF. The decreased IENFDs in sole skins of diabetic mice were ameliorated by exendin-4.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that exendin-4 ameliorates the severity of DPN, which may be achieved by its direct actions on DRG neurons and their axons.
Figures
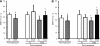
References
-
- Toth C, Brussee V, Cheng C, Zochodne DW. Diabetes mellitus and the sensory neuron. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004;63:561–573 - PubMed
-
- Zochodne DW. Diabetes mellitus and the peripheral nervous system: manifestations and mechanisms. Muscle Nerve 2007;36:144–166 - PubMed
-
- Kles KA, Vinik AI. Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: the case for diabetic neurovascular function as an essential component. Curr Diabetes Rev 2006;2:131–145 - PubMed
-
- Genuth S. Insights from the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study on the use of intensive glycemic treatment to reduce the risk of complications of type 1 diabetes. Endocr Pract 2006;12(Suppl. 1):34–41 - PubMed
-
- Nakae M, Kamiya H, Naruse K, et al. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on experimental diabetic neuropathy in rats. Diabetes 2006;55:1470–1477 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

