Predicting chemotherapy toxicity in older adults with cancer: a prospective multicenter study
- PMID: 21810685
- PMCID: PMC3624700
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.34.7625
Predicting chemotherapy toxicity in older adults with cancer: a prospective multicenter study
Abstract
Purpose: Older adults are vulnerable to chemotherapy toxicity; however, there are limited data to identify those at risk. The goals of this study are to identify risk factors for chemotherapy toxicity in older adults and develop a risk stratification schema for chemotherapy toxicity.
Patients and methods: Patients age ≥ 65 years with cancer from seven institutions completed a prechemotherapy assessment that captured sociodemographics, tumor/treatment variables, laboratory test results, and geriatric assessment variables (function, comorbidity, cognition, psychological state, social activity/support, and nutritional status). Patients were followed through the chemotherapy course to capture grade 3 (severe), grade 4 (life-threatening or disabling), and grade 5 (death) as defined by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
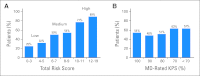
Results: In total, 500 patients with a mean age of 73 years (range, 65 to 91 years) with stage I to IV lung (29%), GI (27%), gynecologic (17%), breast (11%), genitourinary (10%), or other (6%) cancer joined this prospective study. Grade 3 to 5 toxicity occurred in 53% of the patients (39% grade 3, 12% grade 4, 2% grade 5). A predictive model for grade 3 to 5 toxicity was developed that consisted of geriatric assessment variables, laboratory test values, and patient, tumor, and treatment characteristics. A scoring system in which the median risk score was 7 (range, 0 to 19) and risk stratification schema (risk score: percent incidence of grade 3 to 5 toxicity) identified older adults at low (0 to 5 points; 30%), intermediate (6 to 9 points; 52%), or high risk (10 to 19 points; 83%) of chemotherapy toxicity (P < .001).
Conclusion: A risk stratification schema can establish the risk of chemotherapy toxicity in older adults. Geriatric assessment variables independently predicted the risk of toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Smith BD, Smith GL, Hurria A, et al. Future of cancer incidence in the United States: Burdens upon an aging, changing nation. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2758–2765. - PubMed
-
- Hutchins LF, Unger JM, Crowley JJ, et al. Underrepresentation of patients 65 years of age or older in cancer-treatment trials. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:2061–2067. - PubMed
-
- Talarico L, Chen G, Pazdur R. Enrollment of elderly patients in clinical trials for cancer drug registration: A 7-year experience by the US Food and Drug Administration. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4626–4631. - PubMed
-
- Muss HB, Woolf S, Berry D, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy in older and younger women with lymph node-positive breast cancer. JAMA. 2005;293:1073–1081. - PubMed
-
- Sargent DJ, Goldberg RM, Jacobson SD, et al. A pooled analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected colon cancer in elderly patients. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1091–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical