Parcellation in left lateral parietal cortex is similar in adults and children
- PMID: 21810781
- PMCID: PMC3328346
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhr189
Parcellation in left lateral parietal cortex is similar in adults and children
Abstract
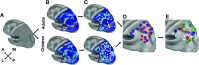
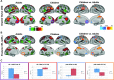
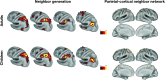
A key question in developmental neuroscience involves understanding how and when the cerebral cortex is partitioned into distinct functional areas. The present study used functional connectivity MRI mapping and graph theory to identify putative cortical areas and generate a parcellation scheme of left lateral parietal cortex (LLPC) in 7 to 10-year-old children and adults. Results indicated that a majority of putative LLPC areas could be matched across groups (mean distance between matched areas across age: 3.15 mm). Furthermore, the boundaries of children's putative LLPC areas respected the boundaries generated from the adults' parcellation scheme for a majority of children's areas (13/15). Consistent with prior research, matched LLPC areas showed age-related differences in functional connectivity strength with other brain regions. These results suggest that LLPC cortical parcellation and functional connectivity mature along different developmental trajectories, with adult-like boundaries between LLPC areas established in school-age children prior to adult-like functional connectivity.
Figures

References
-
- Blakemore SJ, Choudhury S. Development of the adolescent brain: implications for executive function and social cognition. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2006;47:296–312. - PubMed
-
- Brown TT, Lugar HM, Coalson RS, Miezin FM, Petersen SE, Schlaggar BL. Developmental changes in human cerebral functional organization for word generation. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:275–290. - PubMed
-
- Bunge SA, Wright SB. Neurodevelopmental changes in working memory and cognitive control. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007;17:243–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

