Generation and evaluation of a monoclonal antibody, designated MAdL, as a new specific marker for adenocarcinomas of the lung
- PMID: 21811254
- PMCID: PMC3188931
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.281
Generation and evaluation of a monoclonal antibody, designated MAdL, as a new specific marker for adenocarcinomas of the lung
Abstract
Background: Different therapy regimens in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are of rising clinical importance, and therefore a clear-cut subdifferentiation is mandatory. The common immunohistochemical markers available today are well applicable for subdifferentiation, but a fraction of indistinct cases still remains, demanding upgrades of the panel by new markers.
Methods: We report here the generation and evaluation of a new monoclonal antibody carrying the MAdL designation, which was raised against primary isolated human alveolar epithelial cells type 2.
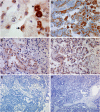
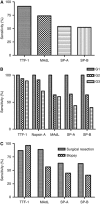
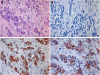
Results: Upon screening, one clone (MAdL) was identified as a marker for alveolar epithelial cell type II, alveolar macrophages and adenocarcinomas of the lung. In a large-scale study, this antibody, with an optimised staining procedure for formalin-fixed tissues, was then evaluated together with the established markers thyroid transcription factor-1, surfactant protein-A, pro-surfactant protein-B and napsin A in a series of 362 lung cancer specimens. The MAdL displays a high specificity (>99%) for adenocarcinomas of the lung, together with a sensitivity of 76.5%, and is capable of delivering independent additional diagnostic information to the established markers.
Conclusion: We conclude that MAdL is a new specific marker for adenocarcinomas of the lung, which helps to clarify subdifferentiation in a considerable portion of NSCLCs.
Figures
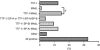
Similar articles
-
Chromogenic immunohistochemical quadruplex provides accurate diagnostic differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020 Apr;45:151454. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2019.151454. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31923744
-
Ribonucleic Acid In Situ Hybridization Is a More Sensitive Method Than Immunohistochemistry in Detection of Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 and Napsin A Expression in Lung Adenocarcinomas.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016 Apr;140(4):332-40. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2014-0644-OA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016. PMID: 27028392
-
Large-scale comparative analyses of immunomarkers for diagnostic subtyping of non-small-cell lung cancer biopsies.Histopathology. 2012 Dec;61(6):1017-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04308.x. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Histopathology. 2012. PMID: 22882703
-
Tissue-sparing application of the newly proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of adenocarcinoma of the lung shows practical diagnostic and prognostic impact.Am J Clin Pathol. 2012 Jun;137(6):946-56. doi: 10.1309/AJCP77KMKJXNMPMS. Am J Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22586054
-
[Non-small cell lung cancer. New biomarkers for diagnostics and therapy].Pathologe. 2015 Nov;36 Suppl 2:189-93. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0084-1. Pathologe. 2015. PMID: 26391246 Review. German.
Cited by
-
[Current issues in pulmonary pathology. Report of the working group on pulmonary pathology of the German Society of Pathology].Pathologe. 2012 Nov;33 Suppl 2:351-4. doi: 10.1007/s00292-012-1644-2. Pathologe. 2012. PMID: 23080028 German.
-
The high diagnostic accuracy of combined test of thyroid transcription factor 1 and Napsin A to distinguish between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 8;9(7):e100837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100837. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25003505 Free PMC article.
-
The study on newly developed McAb NJ001 specific to non-small cell lung cancer and its biological characteristics.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033009. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boggaram V (2003) Regulation of lung surfactant protein gene expression. Front Biosci 8: d751–d764 - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Levin B (2009) World Cancer Report 2008. International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. WHO Press: Geneva
-
- Brasch F, Ochs M, Kahne T, Guttentag S, Schauer-Vukasinovic V, Derrick M, Johnen G, Kapp N, Muller KM, Richter J, Giller T, Hawgood S, Buhling F (2003) Involvement of napsin A in the C- and N-terminal processing of surfactant protein B in type-II pneumocytes of the human lung. J Biol Chem 278: 49006–49014 - PubMed
-
- Chuman Y, Bergman A, Ueno T, Saito S, Sakaguchi K, Alaiya AA, Franzén B, Bergman T, Arnott D, Auer G, Appella E, Jörnvall H, Linder S (1999) Napsin A, a member of the aspartic protease family, is abundantly expressed in normal lung and kidney tissue and is expressed in lung adenocarcinomas. FEBS Lett 462: 129–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

