Discrepancies in reporting the CAG repeat lengths for Huntington's disease
- PMID: 21811303
- PMCID: PMC3234505
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.136
Discrepancies in reporting the CAG repeat lengths for Huntington's disease
Abstract
Huntington's disease results from a CAG repeat expansion within the Huntingtin gene; this is measured routinely in diagnostic laboratories. The European Huntington's Disease Network REGISTRY project centrally measures CAG repeat lengths on fresh samples; these were compared with the original results from 121 laboratories across 15 countries. We report on 1326 duplicate results; a discrepancy in reporting the upper allele occurred in 51% of cases, this reduced to 13.3% and 9.7% when we applied acceptable measurement errors proposed by the American College of Medical Genetics and the Draft European Best Practice Guidelines, respectively. Duplicate results were available for 1250 lower alleles; discrepancies occurred in 40% of cases. Clinically significant discrepancies occurred in 4.0% of cases with a potential unexplained misdiagnosis rate of 0.3%. There was considerable variation in the discrepancy rate among 10 of the countries participating in this study. Out of 1326 samples, 348 were re-analysed by an accredited diagnostic laboratory, based in Germany, with concordance rates of 93% and 94% for the upper and lower alleles, respectively. This became 100% if the acceptable measurement errors were applied. The central laboratory correctly reported allele sizes for six standard reference samples, blind to the known result. Our study differs from external quality assessment (EQA) schemes in that these are duplicate results obtained from a large sample of patients across the whole diagnostic range. We strongly recommend that laboratories state an error rate for their measurement on the report, participate in EQA schemes and use reference materials regularly to adjust their own internal standards.
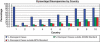
Figures
References
-
- Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell. 1993;72:971–983. - PubMed
-
- Kremer B, Godberg P, Andrew SE, et al. A worldwide study of the Huntington's disease mutation. The sensitivity and specificity of measuring CAG repeats. New Engl J Med. 1994;330:1401–1406. - PubMed
-
- Losekoot M, Bakker B, Laccone F, Stenhouse S, Elles R. A European pilot quality assessment scheme for molecular diagnosis of Huntington's disease. Eur J Hum Genet. 1999;7:217–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

