Linkage analyses of stimulant dependence, craving, and heavy use in American Indians
- PMID: 21812097
- PMCID: PMC3188982
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31218
Linkage analyses of stimulant dependence, craving, and heavy use in American Indians
Abstract
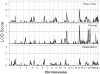
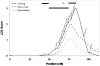
Amphetamine-type substances are the second most widely used illicit drugs in the United States. There is evidence to suggest that stimulant use (cocaine and methamphetamine) has a heritable component, yet the areas of the genome underlying these use disorders are yet to be identified. This study's aims were to map loci linked to stimulant dependence, heavy use, and craving in an American Indian community at high risk for substance dependence. DSM diagnosis of stimulant dependence, as well as indices of stimulant "craving," and "heavy use," were obtained using the Semi-Structured Assessment for the Genetics of Alcoholism (SSAGA). Genotypes were determined for a panel of 791 microsatellite polymorphisms in 381 members of multiplex families using SOLAR. Stimulant dependence, stimulant "craving," and "heavy stimulant use," were all found to be heritable. Analyses of multipoint variance component LOD scores, failed to yield evidence of linkage for stimulant dependence. For the stimulant "craving" phenotype, linkage analysis revealed a locus that had a LOD score of 3.02 on chromosome 15q25.3-26.1 near the nicotinic receptor gene cluster. A LOD score of 2.05 was found at this same site for "heavy stimulant use." Additional loci with LOD scores above 2.00 were found for stimulant "craving" on chromosomes 12p13.33-13.32 and 18q22.3. These results corroborate the importance of "craving" as an important phenotype that is associated with regions on chromosome 12, 15, and 18, that have been highlighted in prior segregation studies in this and other populations for substance dependence-related phenotypes.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. Merlin--rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnosis and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-III-R) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1987.
-
- Amos CI, Krushkal J, Thiel TJ, Young A, Zhu DK, Boerwinkle E, de Andrade M. Comparison of model-free linkage mapping strategies for the study of a complex trait. Genetic Epidemiology. 1997;14:743–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

