Safety and efficacy of vagus nerve stimulation in fibromyalgia: a phase I/II proof of concept trial
- PMID: 21812908
- PMCID: PMC3173600
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2011.01203.x
Safety and efficacy of vagus nerve stimulation in fibromyalgia: a phase I/II proof of concept trial
Abstract
Objective: We performed an open-label Phase I/II trial to evaluate the safety and tolerability of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in patients with treatment-resistant fibromyalgia (FM) as well as to determine preliminary measures of efficacy in these patients.
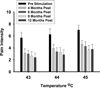
Methods: Of 14 patients implanted with the VNS stimulator, 12 patients completed the initial 3-month study of VNS; 11 patients returned for follow-up visits 5, 8, and 11 months after start of stimulation. Therapeutic efficacy was assessed with a composite measure requiring improvement in pain, overall wellness, and physical function. Loss of both pain and tenderness criteria for the diagnosis of FM was added as a secondary outcome measure because of results found at the end of 3 months of stimulation.
Results: Side effects were similar to those reported in patients treated with VNS for epilepsy or depression and, in addition, dry mouth and fatigue were reported. Two patients did not tolerate stimulation. At 3 months, five patients had attained efficacy criteria; of these, two patients no longer met widespread pain or tenderness criteria for the diagnosis of FM. The therapeutic effect seemed to increase over time in that additional participants attained both criteria at 11 months.
Conclusions: Side effects and tolerability were similar to those found in disorders currently treated with VNS. Preliminary outcome measures suggested that VNS may be a useful adjunct treatment for FM patients resistant to conventional therapeutic management, but further research is required to better understand its actual role in the treatment of FM.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00294281.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A pilot study of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) for treatment-resistant anxiety disorders.Brain Stimul. 2008 Apr;1(2):112-21. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2008.02.001. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Brain Stimul. 2008. PMID: 20633378
-
A novel implantable vagus nerve stimulation system (ADNS-300) for combined stimulation and recording of the vagus nerve: pilot trial at Ghent University Hospital.Epilepsy Res. 2010 Dec;92(2-3):231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Epilepsy Res. 2010. PMID: 21071177 Clinical Trial.
-
Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Epilepsy in Patients With Sturge-Weber Syndrome: A Pilot Study.Pediatr Neurol. 2025 Mar;164:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2024.12.016. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Pediatr Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39848141
-
Electrical stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2013 Oct 1;13(18):1-37. eCollection 2013. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2013. PMID: 24228081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation: Surgical technique of implantation and revision and related morbidity.Epilepsia. 2017 Apr;58 Suppl 1:85-90. doi: 10.1111/epi.13678. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28386925 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic Diffuse Pain and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders After Traumatic Stress: Pathophysiology Through a Polyvagal Perspective.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 May 31;5:145. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00145. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29904631 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Histological Effects of Chronic Neural Electrode Implantation.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2017 Feb 6;2(2):80-93. doi: 10.1002/lio2.66. eCollection 2017 Apr. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28894826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture treatment of vascular cognitive impairment through peripheral nerve stimulation pathway: a scoping review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Apr 28;17:1515327. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1515327. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40357233 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of transauricular vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled exploratory study.Neurol Sci. 2024 May;45(5):2289-2300. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07229-2. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38063922 Clinical Trial.
-
Both high fat and high carbohydrate diets impair vagus nerve signaling of satiety.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89465-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Hebert L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Randich A, Gebhart GF. Vagal afferent modulation of nociception. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1992;17:77–99. - PubMed
-
- Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, Lalonde JK, Sandhu HS, Keck PE, Jr., et al. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1336–1344. - PubMed
-
- Russell IJ, Mease PJ, Smith TR, Kajdasz DK, Wohlreich MM, Detke MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine for treatment of fibromyalgia in patients with or without major depressive disorder: Results from a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trial. Pain. 2008;136:432–444. - PubMed
-
- Borckardt JJ, Kozel FA, Anderson B, Walker A, George MS. Vagus nerve stimulation affects pain perception in depressed adults. Pain Res Manag. 2005;10:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous