Long-term exposure to hypoxia inhibits tumor progression of lung cancer in rats and mice
- PMID: 21812995
- PMCID: PMC3199866
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-331
Long-term exposure to hypoxia inhibits tumor progression of lung cancer in rats and mice
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia has been identified as a major negative factor for tumor progression in clinical observations and in animal studies. However, the precise role of hypoxia in tumor progression has not been fully explained. In this study, we extensively investigated the effect of long-term exposure to hypoxia on tumor progression in vivo.
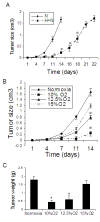
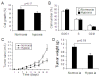
Methods: Rats bearing transplanted tumors consisting of A549 human lung cancer cells (lung cancer tumor) were exposed to hypoxia for different durations and different levels of oxygen. The tumor growth and metastasis were evaluated. We also treated A549 lung cancer cells (A549 cells) with chronic hypoxia and then implanted the hypoxia-pretreated cancer cells into mice. The effect of exposure to hypoxia on metastasis of Lewis lung carcinoma in mice was also investigated.
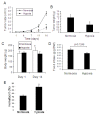
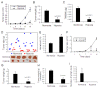
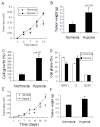
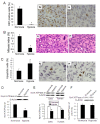
Results: We found that long-term exposure to hypoxia a) significantly inhibited lung cancer tumor growth in xenograft and orthotopic models in rats, b) significantly reduced lymphatic metastasis of the lung cancer in rats and decreased lung metastasis of Lewis lung carcinoma in mice, c) reduced lung cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in vitro, d) decreased growth of the tumors from hypoxia-pretreated A549 cells, e) decreased Na+-K+ ATPase α1 expression in hypoxic lung cancer tumors, and f) increased expression of hypoxia inducible factors (HIF1α and HIF2α) but decreased microvessel density in the lung cancer tumors. In contrast to lung cancer, the growth of tumor from HCT116 human colon cancer cells (colon cancer tumor) was a) significantly enhanced in the same hypoxia conditions, accompanied by b) no significant change in expression of Na+-K+ ATPase α1, c) increased HIF1α expression (no HIF2α was detected) and d) increased microvessel density in the tumor tissues.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that long-term exposure to hypoxia repressed tumor progression of the lung cancer from A549 cells and that decreased expression of Na+-K+ ATPase was involved in hypoxic inhibition of tumor progression. The results from this study provide new insights into the role of hypoxia in tumor progression and therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

