Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L
- PMID: 21813458
- PMCID: PMC3241635
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr586
Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L
Abstract
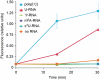
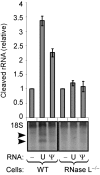
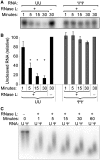
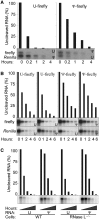
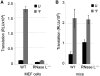
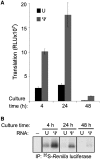
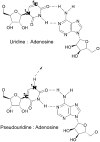
The interferon-induced enzymes 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) and RNase L are key components of innate immunity involved in sensory and effector functions following viral infections. Upon binding target RNA, OAS is activated to produce 2'-5'-linked oligoadenylates (2-5A) that activate RNase L, which then cleaves single-stranded self and non-self RNA. Modified nucleosides that are present in cellular transcripts have been shown to suppress activation of several RNA sensors. Here, we demonstrate that in vitro transcribed, unmodified RNA activates OAS, induces RNase L-mediated ribosomal RNA (rRNA) cleavage and is rapidly cleaved by RNase L. In contrast, RNA containing modified nucleosides activates OAS less efficiently and induces limited rRNA cleavage. Nucleoside modifications also make RNA resistant to cleavage by RNase L. Examining translation in RNase L(-/-) cells and mice confirmed that RNase L activity reduces translation of unmodified mRNA, which is not observed with modified mRNA. Additionally, mRNA containing the nucleoside modification pseudouridine is translated longer and has an extended half-life. The observation that modified nucleosides in RNA reduce 2-5A pathway activation joins OAS and RNase L to the list of RNA sensors and effectors whose functions are limited when RNA is modified, confirming the role of nucleoside modifications in suppressing immune recognition of RNA.
Figures
References
-
- Lane BG. Historical perspective on RNA nucleoside modifications. In: Grosjean H, Benne R, editors. Modification and Editing of RNA. Washington DC: ASM Press; 1998. pp. 1–20.
-
- Charette M, Gray MW. Pseudouridine in RNA: what, where, how, and why. IUBMB Life. 2000;49:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

