Gadd45a sensitizes medulloblastoma cells to irradiation and suppresses MMP-9-mediated EMT
- PMID: 21813510
- PMCID: PMC3177664
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor109
Gadd45a sensitizes medulloblastoma cells to irradiation and suppresses MMP-9-mediated EMT
Abstract
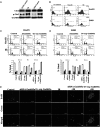
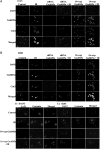
Medulloblastomas are the most common malignant tumors of the central nervous system during childhood. Radiation-induced medulloblastoma tumor recurrences are aggressive and metastatic in nature. In the present study, we demonstrate that Gadd45a expression can sensitize medulloblastoma cells to radiotherapy. We have elucidated the role of Gadd45a in ionizing radiation (IR)-induced G2-M arrest and invasion and metastatic potential of the medulloblastoma cancer cell lines DAOY and D283. We demonstrate that Gadd45a is induced by IR and results in p53 phosphorylation. The role of IR-induced Gadd45a in G2-M arrest is demonstrated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis in the cells treated with siRNA Gadd45a and Ov-exp Gadd45a. We show that Ov-exp Gadd45a aggravates G2-M blockage and also increases binding of Gadd45a to Cdc2 by immunocytochemistry analysis. Furthermore, we show the anti-tumorigenic role of Gadd45a to be mediated by the negative regulation of IR-induced cancer cell invasion and migration-associated proteins, such as matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)-9 and β-catenin. When compared with IR treatment alone, Ov-exp Gadd45a plus IR treatment resulted in decreased nuclear localization and increased membrane localization of β-catenin, and this was further confirmed by membrane distribution. We also show that Ov-exp Gadd45a resulted in downregulation of MMP-9 and suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Alternatively, inhibition of MMP-9 (pM) resulted in upregulation of Gadd45a and suppression of EMT. The anti-tumor effect of pM was correlated with increased expression of Gadd45a protein in nude mice intracranial tumors. Taken together, our studies demonstrate that upregulation of Gadd45a or suppression of MMP-9 (pM) with IR retards medulloblastoma tumor metastatic potential.
Figures




Similar articles
-
siRNA-mediated downregulation of MMP-9 and uPAR in combination with radiation induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest in Medulloblastoma.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Jan;9(1):51-66. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0399. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. Retraction in: Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;19(7):1247. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0395. PMID: 21148633 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Irradiation-induced angiogenesis is associated with an MMP-9-miR-494-syndecan-1 regulatory loop in medulloblastoma cells.Oncogene. 2014 Apr 10;33(15):1922-33. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.151. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23728345
-
Reactivation of death receptor 4 (DR4) expression sensitizes medulloblastoma cell lines to TRAIL.J Neurooncol. 2009 Jul;93(3):303-18. doi: 10.1007/s11060-008-9788-x. Epub 2009 Jan 16. J Neurooncol. 2009. PMID: 19148581 Free PMC article.
-
Minichromosome maintenance proteins 2, 3 and 7 in medulloblastoma: overexpression and involvement in regulation of cell migration and invasion.Oncogene. 2010 Oct 7;29(40):5475-89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.287. Epub 2010 Jul 26. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20661220
-
Overexpressed TP73 induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma.BMC Cancer. 2007 Jul 12;7:127. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-127. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17626635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes the metastasis of colorectal cancer by inducing the epithelial‑mesenchymal transition mediated by the FAK/AKT/MMPs axis.Int J Oncol. 2019 Jan;54(1):41-52. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4607. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30365116 Free PMC article.
-
Low Expression of miR-466f-3p Sustains Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Sonic Hedgehog Medulloblastoma Stem Cells Through Vegfa-Nrp2 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 12;9:1281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01281. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30483126 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of lysyl oxidase‑like 2 inhibits the migration, invasion and epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells through the Src/FAK signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2019 May;54(5):1676-1690. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4726. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30816490 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin decreases invasiveness, deactivates STAT3 signaling, and reverses interleukin-6 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and matrix metalloproteinase secretion of pancreatic cancer cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Oct 19;8:2989-3001. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S91511. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26527884 Free PMC article.
-
Paeoniflorin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Glioblastoma Cells via Suppression Transforming Growth Factor β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Neurochem Res. 2018 Mar;43(3):760-774. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2478-y. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29423667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutkowski S, Cohen B, Finlay J, et al. Medulloblastoma in young children. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;54:635–637. doi:10.1002/pbc.22372. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reddick WE, Russell JM, Glass JO, et al. Subtle white matter volume differences in children treated for medulloblastoma with conventional or reduced dose craniospinal irradiation. Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;18:787–793. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(00)00182-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rutkowski S, Bode U, Deinlein F, et al. Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy alone. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:978–986. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa042176. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ris MD, Packer R, Goldwein J, Jones-Wallace D, Boyett JM. Intellectual outcome after reduced-dose radiation therapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy for medulloblastoma: a Children's Cancer Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3470–3476. - PubMed
-
- Fu KK, Phillips TL. Biologic rationale of combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991;5:737–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

