A comprehensively molecular haplotype-resolved genome of a European individual
- PMID: 21813624
- PMCID: PMC3202284
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.125047.111
A comprehensively molecular haplotype-resolved genome of a European individual
Abstract
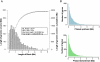
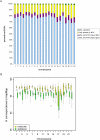
Independent determination of both haplotype sequences of an individual genome is essential to relate genetic variation to genome function, phenotype, and disease. To address the importance of phase, we have generated the most complete haplotype-resolved genome to date, "Max Planck One" (MP1), by fosmid pool-based next generation sequencing. Virtually all SNPs (>99%) and 80,000 indels were phased into haploid sequences of up to 6.3 Mb (N50 ~1 Mb). The completeness of phasing allowed determination of the concrete molecular haplotype pairs for the vast majority of genes (81%) including potential regulatory sequences, of which >90% were found to be constituted by two different molecular forms. A subset of 159 genes with potentially severe mutations in either cis or trans configurations exemplified in particular the role of phase for gene function, disease, and clinical interpretation of personal genomes (e.g., BRCA1). Extended genomic regions harboring manifold combinations of physically and/or functionally related genes and regulatory elements were resolved into their underlying "haploid landscapes," which may define the functional genome. Moreover, the majority of genes and functional sequences were found to contain individual or rare SNPs, which cannot be phased from population data alone, emphasizing the importance of molecular phasing for characterizing a genome in its molecular individuality. Our work provides the foundation to understand that the distinction of molecular haplotypes is essential to resolve the (inherently individual) biology of genes, genomes, and disease, establishing a reference point for "phase-sensitive" personal genomics. MP1's annotated haploid genomes are available as a public resource.
Figures



References
-
- Bansal V, Bafna V 2008. HapCUT: An efficient and accurate algorithm for the haplotype assembly problem. Bioinformatics 24: i153–i159 - PubMed
-
- Bansal V, Tewhey R, Topol EJ, Schork NJ 2011. The next phase in human genetics. Nat Biotechnol 29: 38–39 - PubMed
-
- Beissbarth T, Speed TP 2004. GOstat: Find statistically overrepresented Gene Ontologies within a group of genes. Bioinformatics 20: 1464–1465 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
