A conformational change of C fragment of tetanus neurotoxin reduces its ganglioside-binding activity but does not destroy its immunogenicity
- PMID: 21813664
- PMCID: PMC3187031
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.05244-11
A conformational change of C fragment of tetanus neurotoxin reduces its ganglioside-binding activity but does not destroy its immunogenicity
Abstract
The C fragment of tetanus neurotoxin (TeNT-Hc) with different conformations was observed due to the four cysteine residues within it which could form different intramolecular disulfide bonds. In this study, we prepared and compared three types of monomeric TeNT-Hc with different conformational components: free sulfhydryls (50 kDa), bound sulfhydryls (44 kDa), and a mixture of the two conformational proteins (half 50 kDa and half 44 kDa). TeNT-Hc with bound sulfhydryls reduced its binding activity to ganglioside G(T1b) and neuronal PC-12 cells compared to what was seen for TeNT-Hc with free sulfhydryls. However, there was no significant difference among their immunogenicities in mice, including induction of antitetanus toxoid IgG titers, antibody types, and protective capacities against tetanus neurotoxin challenge. Our results showed that the conformational changes of TeNT-Hc resulting from disulfide bond formation reduced its ganglioside-binding activity but did not destroy its immunogenicity, and the protein still retained continuous B cell and T cell epitopes; that is, the presence of the ganglioside-binding site within TeNT-Hc may be not essential for the induction of a fully protective antitetanus response. TeNT-Hc with bound sulfhydryls may be developed into an ideal human vaccine with a lower potential for side effects.
Figures

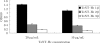


References
-
- Emsley P., et al. 2000. The structures of the HC fragment of tetanus toxin with carbohydrate subunit complexes provide insight into ganglioside binding. J. Biol. Chem. 275:8889–8894 - PubMed
-
- Fishman P. S., Carrigan D. R. 1987. Retrograde transneuronal transfer of the C-fragment of tetanus toxin. Brain Res. 406:275–279 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

