An international collaboration to standardize HIV-2 viral load assays: results from the 2009 ACHI(E)V(2E) quality control study
- PMID: 21813718
- PMCID: PMC3187346
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02389-10
An international collaboration to standardize HIV-2 viral load assays: results from the 2009 ACHI(E)V(2E) quality control study
Abstract
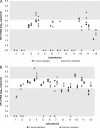
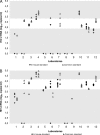
Accurate HIV-2 plasma viral load quantification is crucial for adequate HIV-2 patient management and for the proper conduct of clinical trials and international cohort collaborations. This study compared the homogeneity of HIV-2 RNA quantification when using HIV-2 assays from ACHI(E)V(2E) study sites and either in-house PCR calibration standards or common viral load standards supplied to all collaborators. Each of the 12 participating laboratories quantified blinded HIV-2 samples, using its own HIV-2 viral load assay and standard as well as centrally validated and distributed common HIV-2 group A and B standards (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/sequence/HelpDocs/subtypes-more.html). Aliquots of HIV-2 group A and B strains, each at 2 theoretical concentrations (2.7 and 3.7 log(10) copies/ml), were tested. Intralaboratory, interlaboratory, and overall variances of quantification results obtained with both standards were compared using F tests. For HIV-2 group A quantifications, overall and interlaboratory and/or intralaboratory variances were significantly lower when using the common standard than when using in-house standards at the concentration levels of 2.7 log(10) copies/ml and 3.7 log(10) copies/ml, respectively. For HIV-2 group B, a high heterogeneity was observed and the variances did not differ according to the type of standard used. In this international collaboration, the use of a common standard improved the homogeneity of HIV-2 group A RNA quantification only. The diversity of HIV-2 group B, particularly in PCR primer-binding regions, may explain the heterogeneity in quantification of this strain. Development of a validated HIV-2 viral load assay that accurately quantifies distinct circulating strains is needed.
Figures

References
-
- Benard A., et al. 2011. Immunovirological response to triple nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitors and ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors in treatment-naive HIV-2-infected patients: the ACHIEV2E Collaboration Study Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 52:1257–1266 - PubMed
-
- Borget M. Y., Diallo K., Adje-Toure C., Chorba T., Nkengasong J. N. 2009. Virologic and immunologic responses to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-1 and HIV-2 dually infected patients: case reports from Abidjan, Cote d'Ivoire. J. Clin. Virol. 45:72–75 - PubMed
-
- Damond F., Apetrei C., Descamps D., Brun-Vezinet F., Simon F. 1999. HIV-1 subtypes and plasma RNA quantification. AIDS 13:286–288 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

