Pythium aphanidermatum infection following combat trauma
- PMID: 21813724
- PMCID: PMC3187319
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01209-11
Pythium aphanidermatum infection following combat trauma
Abstract
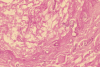
Pythium aphanidermatum is a fungus-like plant pathogen which has never been reported as a cause of human infection. We report a case of P. aphanidermatum invasive wound infection in a 21-year-old male injured during combat operations in Afghanistan.
Figures

References
-
- Blaschek W., Kasbauer J., Kraus J., Franz G. 1992. Pythium aphanidermatum: culture, cell-wall composition, and isolation and structure of antitumour storage and solubilised cell-wall (1→3),(1→6) beta-d-glucans. Carbohydr. Res. 231:293–307 - PubMed
-
- Camus A., Grooters A., Aquilar R. 2004. Granulomatous pneumonia caused by Pythium insidiosum in a Central American jaguar, Panthera onca. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 16:567–571 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi, 2nd ed Approved standard M38-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
-
- El-Tarabily K. A., Nassar A. H., Hardy G. E., Sivasithamparam K. 2009. Plant growth promotion and biological control of Pythium aphanidermatum, a pathogen of cucumber, by endophytic actinomycetes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 106:13–26 - PubMed
-
- Heine G., Tikum G., Horst W. 2007. The effect of silicon on the infection by and spread of Pythium aphanidermatum in single roots of tomato and bitter gourd. J. Exp. Bot. 58:569–577 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

