Replication and explorations of high-order epistasis using a large advanced intercross line pedigree
- PMID: 21814519
- PMCID: PMC3140984
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002180
Replication and explorations of high-order epistasis using a large advanced intercross line pedigree
Abstract
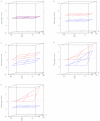
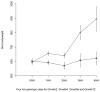
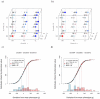
Dissection of the genetic architecture of complex traits persists as a major challenge in biology; despite considerable efforts, much remains unclear including the role and importance of genetic interactions. This study provides empirical evidence for a strong and persistent contribution of both second- and third-order epistatic interactions to long-term selection response for body weight in two divergently selected chicken lines. We earlier reported a network of interacting loci with large effects on body weight in an F(2) intercross between these high- and low-body weight lines. Here, most pair-wise interactions in the network are replicated in an independent eight-generation advanced intercross line (AIL). The original report showed an important contribution of capacitating epistasis to growth, meaning that the genotype at a hub in the network releases the effects of one or several peripheral loci. After fine-mapping of the loci in the AIL, we show that these interactions were persistent over time. The replication of five of six originally reported epistatic loci, as well as the capacitating epistasis, provides strong empirical evidence that the originally observed epistasis is of biological importance and is a contributor in the genetic architecture of this population. The stability of genetic interaction mechanisms over time indicates a non-transient role of epistasis on phenotypic change. Third-order epistasis was for the first time examined in this study and was shown to make an important contribution to growth, which suggests that the genetic architecture of growth is more complex than can be explained by two-locus interactions only. Our results illustrate the importance of designing studies that facilitate exploration of epistasis in populations for obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the genetics underlying a complex trait.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Andersson L, Georges M. Domestic-animal genomics: deciphering the genetics of complex traits. Nature reviews. Genetics. 2004;5:202–12. - PubMed
-
- Evans DM, Marchini J, Morris AP, Cardon LR. Two-stage two-locus models in genome-wide association. PLoS Genet. 2006;2:e157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perola M, Sammalisto S, Hiekkalinna T, Martin NG, Visscher PM, et al. Combined genome scans for body stature in 6,602 European twins: evidence for common Caucasian loci. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e97. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang X-S, Hill WG. Change and maintenance of variation in quantitative traits in the context of the Price equation. Theoretical population biology. 2010;77:14–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

