Quantitative RNA-seq analysis of the Campylobacter jejuni transcriptome
- PMID: 21816880
- PMCID: PMC3353397
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.050278-0
Quantitative RNA-seq analysis of the Campylobacter jejuni transcriptome
Abstract
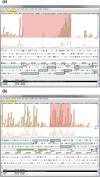
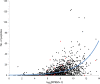
Campylobacter jejuni is the most common bacterial cause of foodborne disease in the developed world. Its general physiology and biochemistry, as well as the mechanisms enabling it to colonize and cause disease in various hosts, are not well understood, and new approaches are required to understand its basic biology. High-throughput sequencing technologies provide unprecedented opportunities for functional genomic research. Recent studies have shown that direct Illumina sequencing of cDNA (RNA-seq) is a useful technique for the quantitative and qualitative examination of transcriptomes. In this study we report RNA-seq analyses of the transcriptomes of C. jejuni (NCTC11168) and its rpoN mutant. This has allowed the identification of hitherto unknown transcriptional units, and further defines the regulon that is dependent on rpoN for expression. The analysis of the NCTC11168 transcriptome was supplemented by additional proteomic analysis using liquid chromatography-MS. The transcriptomic and proteomic datasets represent an important resource for the Campylobacter research community.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215, 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate – a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57, 289–300.
-
- Carrillo C. D., Taboada E., Nash J. H., Lanthier P., Kelly J., Lau P. C., Verhulp R., Mykytczuk O., Sy J., et al. & other authors (2004). Genome-wide expression analyses of Campylobacter jejuni NCTC11168 reveals coordinate regulation of motility and virulence by flhA. J Biol Chem 279, 20327–20338. 10.1074/jbc.M401134200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

