Mutations in CIC and FUBP1 contribute to human oligodendroglioma
- PMID: 21817013
- PMCID: PMC3170506
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1210557
Mutations in CIC and FUBP1 contribute to human oligodendroglioma
Abstract
Oligodendrogliomas are the second most common malignant brain tumor in adults and exhibit characteristic losses of chromosomes 1p and 19q. To identify the molecular genetic basis for this alteration, we performed exomic sequencing of seven tumors. Among other changes, we found that the CIC gene (homolog of the Drosophila gene capicua) on chromosome 19q was somatically mutated in six cases and that the FUBP1 gene [encoding far-upstream element (FUSE) binding protein] on chromosome 1p was somatically mutated in two tumors. Examination of 27 additional oligodendrogliomas revealed 12 and 3 more tumors with mutations of CIC and FUBP1, respectively, 58% of which were predicted to result in truncations of the encoded proteins. These results suggest a critical role for these genes in the biology and pathology of oligodendrocytes.
Figures
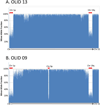
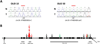
References
-
- Coons SW, Johnson PC, Scheithauer BW, Yates AJ, Pearl DK. Cancer. 1997;79:1381. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JE, van den Bent MJ. Oncologist. 2009;14:155. - PubMed
-
- Maintz D, et al. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997;56:1098. - PubMed
-
- Smith JS, et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18:636. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins RB, et al. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS20023/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA62924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA121113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140316/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA43460/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11898/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2DE020957/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA057345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA011898/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA57345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA043460/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS020023/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-43302/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA121113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA062924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009574/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DE020957/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN043302/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

