Novel oxysterols observed in tissues and fluids of AY9944-treated rats: a model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
- PMID: 21817059
- PMCID: PMC3173002
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M018366
Novel oxysterols observed in tissues and fluids of AY9944-treated rats: a model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Abstract
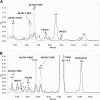
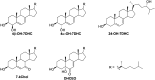
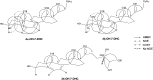
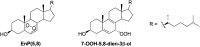
Treatment of Sprague-Dawley rats with AY9944, an inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysterol-Δ(7)-reductase (Dhcr7), leads to elevated levels of 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) and reduced levels of cholesterol in all biological tissues, mimicking the key biochemical hallmark of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS). Fourteen 7-DHC-derived oxysterols previously have been identified as products of free radical oxidation in vitro; one of these oxysterols, 3β,5α-dihydroxycholest-7-en-6-one (DHCEO), was recently identified in Dhcr7-deficient cells and in brain tissues of Dhcr7-null mouse. We report here the isolation and characterization of three novel 7-DHC-derived oxysterols (4α- and 4β-hydroxy-7-DHC and 24-hydroxy-7-DHC) in addition to DHCEO and 7-ketocholesterol (7-kChol) from the brain tissues of AY9944-treated rats. The identities of these five oxysterols were elucidated by HPLC-ultraviolet (UV), HPLC-MS, and 1D- and 2D-NMR. Quantification of 4α- and 4β-hydroxy-7-DHC, DHCEO, and 7-kChol in rat brain, liver, and serum were carried out by HPLC-MS using d(7)-DHCEO as an internal standard. With the exception of 7-kChol, these oxysterols were present only in tissues of AY9944-treated, but not control rats, and 7-kChol levels were markedly (>10-fold) higher in treated versus control rats. These findings are discussed in the context of the potential involvement of 7-DHC-derived oxysterols in the pathogenesis of SLOS.
Figures


References
-
- Irons M., Elias E. R., Salen G., Tint G. S., Batta A. K. 1993. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Lancet. 341: 1414. - PubMed
-
- Tint G. S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Batta A. K., Frieden R., Chen T. S., Salen G. 1994. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 330: 107–113. - PubMed
-
- Fitzky B. U., Moebius F. F., Asaoka H., Waage-Baudet H., Xu L., Xu G., Maeda N., Kluckman K., Hiller S., Yu H., et al. 2001. 7-Dehydrocholesterol-dependent proteolysis of HMG-CoA reductase suppresses sterol biosynthesis in a mouse model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz/RSH syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 108: 905–915. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krakowiak P. A., Nwokoro N. A., Wassif C. A., Battaile K. P., Nowaczyk M. J., Connor W. E., Maslen C., Steiner R. D., Porter F. D. 2000. Mutation analysis and description of sixteen RSH/Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome patients: polymerase chain reaction-based assays to simplify genotyping. Am. J. Med. Genet. 94: 214–227. - PubMed
-
- Waterham H. R. 2002. Inherited disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis. Clin. Genet. 61: 393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

