Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants protect skeletal muscle against immobilization-induced muscle atrophy
- PMID: 21817113
- PMCID: PMC3220313
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00591.2011
Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants protect skeletal muscle against immobilization-induced muscle atrophy
Abstract
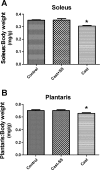
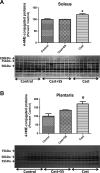
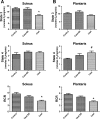
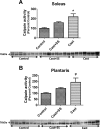
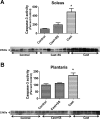
Prolonged periods of muscular inactivity (e.g., limb immobilization) result in skeletal muscle atrophy. Although it is established that reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a role in inactivity-induced skeletal muscle atrophy, the cellular pathway(s) responsible for inactivity-induced ROS production remain(s) unclear. To investigate this important issue, we tested the hypothesis that elevated mitochondrial ROS production contributes to immobilization-induced increases in oxidative stress, protease activation, and myofiber atrophy in skeletal muscle. Cause-and-effect was determined by administration of a novel mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant (SS-31) to prevent immobilization-induced mitochondrial ROS production in skeletal muscle fibers. Compared with ambulatory controls, 14 days of muscle immobilization resulted in significant muscle atrophy, along with increased mitochondrial ROS production, muscle oxidative damage, and protease activation. Importantly, treatment with a mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant attenuated the inactivity-induced increase in mitochondrial ROS production and prevented oxidative stress, protease activation, and myofiber atrophy. These results support the hypothesis that redox disturbances contribute to immobilization-induced skeletal muscle atrophy and that mitochondria are an important source of ROS production in muscle fibers during prolonged periods of inactivity.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson EJ, Lustig ME, Boyle KE, Woodlief TL, Kane DA, Lin CT, Price JW, 3rd, Kang L, Rabinovitch PS, Szeto HH, Houmard JA, Cortright RN, Wasserman DH, Neufer PD. Mitochondrial H2O2 emission and cellular redox state link excess fat intake to insulin resistance in both rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 119: 573–581, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betters JL, Criswell DS, Shanely RA, Van Gammeren D, Falk D, Deruisseau KC, Deering M, Yimlamai T, Powers SK. Trolox attenuates mechanical ventilation-induced diaphragmatic dysfunction and proteolysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170: 1179–1184, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Cherednichenko G, Zima AV, Feng W, Schaefer S, Blatter LA, Pessah IN. NADH oxidase activity of rat cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum regulates calcium-induced calcium release. Circ Res 94: 478–486, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Goldspink DF, Morton AJ, Loughna P, Goldspink G. The effect of hypokinesia and hypodynamia on protein turnover and the growth of four skeletal muscles of the rat. Pflügers Arch 407: 333–340, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol Rev 83: 731–801, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

